Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology ›› 2020, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 850-860.doi: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2020.087
• Special Column • Previous Articles
Pei-Rong LI1,2( ), Gao-Man CHEN1,2, Xue-Qing YANG1,2,***(
), Gao-Man CHEN1,2, Xue-Qing YANG1,2,***( )
)
Received:2020-03-12
Accepted:2020-05-17
Online:2020-07-27
Published:2020-09-02
Contact:
Xue-Qing YANG
E-mail:lpr666lpr@126.com;sling233@hotmail.com
Pei-Rong LI, Gao-Man CHEN, Xue-Qing YANG. Molecular cloning and expression profiles of NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase (CPR) gene in the codling moth, Cydia pomonella[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2020, 57(4): 850-860.
| 基因Gene | 引物序列(5¢-3¢) Primer sequence | 用途Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| CpCPR-ORF | F:ATGCACGTTTTGAAAATGAGTACAG | ORF克隆 TA克隆测序 |
| R:CTATGTTCTCGGGACGAAGCGGACA | ||
| M13 | F:GTTTTCCCAGTCACGAC | |
| R:CAGGAAACAGCTATGAC | ||
| CpCPR | F:AGTCTATGAAGTGGGTTTGGG | RT-qPCR |
| R:GCTCCTCCTCGCCTGTG | ||
| β-Actin | F:CGGCATCCACGAAACCACCT | |
| R:TGGAAGGAGCCAGTGCGG |
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| 基因Gene | 引物序列(5¢-3¢) Primer sequence | 用途Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| CpCPR-ORF | F:ATGCACGTTTTGAAAATGAGTACAG | ORF克隆 TA克隆测序 |
| R:CTATGTTCTCGGGACGAAGCGGACA | ||
| M13 | F:GTTTTCCCAGTCACGAC | |
| R:CAGGAAACAGCTATGAC | ||
| CpCPR | F:AGTCTATGAAGTGGGTTTGGG | RT-qPCR |
| R:GCTCCTCCTCGCCTGTG | ||
| β-Actin | F:CGGCATCCACGAAACCACCT | |
| R:TGGAAGGAGCCAGTGCGG |
| 氨基酸 Amino acid | 数量 Number | 比例(%)Composition | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 数量 Number | 比例(%)Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丙氨酸Ala | 44 | 6.44 | 亮氨酸Leu | 67 | 9.81 |
| 精氨酸Arg | 31 | 4.54 | 赖氨酸Lys | 49 | 7.17 |
| 天冬氨酸Asp | 43 | 6.30 | 甲硫氨酸Met | 14 | 2.05 |
| 天冬酰胺Asn | 28 | 4.10 | 苯丙氨酸Phe | 26 | 3.81 |
| 半胱氨酸Cys | 11 | 1.61 | 脯氨酸Pro | 31 | 4.54 |
| 谷氨酰胺Gln | 27 | 3.95 | 丝氨酸Ser | 40 | 5.86 |
| 谷氨酸Glu | 55 | 8.05 | 苏氨酸Thr | 37 | 5.42 |
| 甘氨酸Gly | 45 | 6.59 | 色氨酸Trp | 10 | 1.46 |
| 组氨酸His | 18 | 2.64 | 络氨酸Tyr | 27 | 3.95 |
| 异亮氨酸Ile | 37 | 5.42 | 缬氨酸Val | 43 | 6.30 |
Table 2 The amino acid composition of CpCPR protein in Cydia pomonella
| 氨基酸 Amino acid | 数量 Number | 比例(%)Composition | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 数量 Number | 比例(%)Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丙氨酸Ala | 44 | 6.44 | 亮氨酸Leu | 67 | 9.81 |
| 精氨酸Arg | 31 | 4.54 | 赖氨酸Lys | 49 | 7.17 |
| 天冬氨酸Asp | 43 | 6.30 | 甲硫氨酸Met | 14 | 2.05 |
| 天冬酰胺Asn | 28 | 4.10 | 苯丙氨酸Phe | 26 | 3.81 |
| 半胱氨酸Cys | 11 | 1.61 | 脯氨酸Pro | 31 | 4.54 |
| 谷氨酰胺Gln | 27 | 3.95 | 丝氨酸Ser | 40 | 5.86 |
| 谷氨酸Glu | 55 | 8.05 | 苏氨酸Thr | 37 | 5.42 |
| 甘氨酸Gly | 45 | 6.59 | 色氨酸Trp | 10 | 1.46 |
| 组氨酸His | 18 | 2.64 | 络氨酸Tyr | 27 | 3.95 |
| 异亮氨酸Ile | 37 | 5.42 | 缬氨酸Val | 43 | 6.30 |
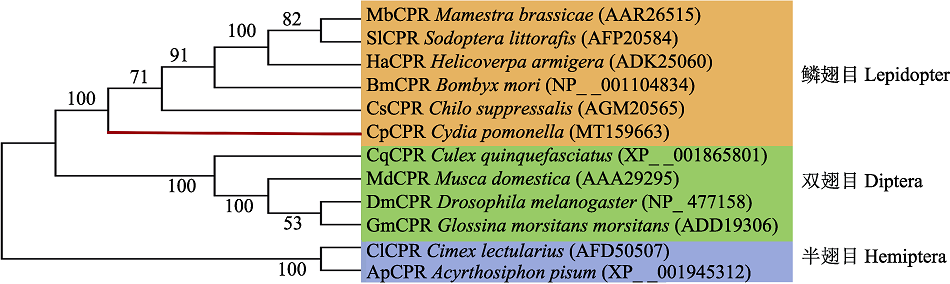
Fig. 6 Phylogenetic relationship of Cydia pomonella CpCPR with CPR from other insects amino acid sequence by neighbor-joining method (1 000 replicates) Different colors represent different insects. Yellow, green, and blue represent insects in Lepidoptera, Diptera, and Hemiptera, respectively; The CPR sequence of codling moth is marked with red lines.
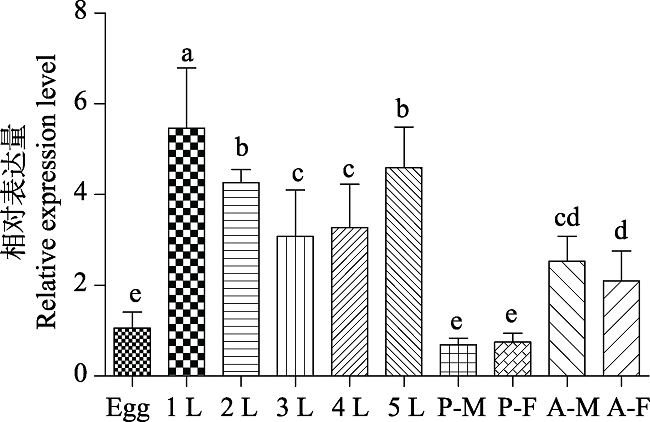
Fig. 7 Expression profiles of CpCPR in different developmental stages of Cydia pomonnella Egg: Egg; 1-5L: 1st-5th instar larva; P-M: Male pupa; P-F: Female pupa; A-M: Male adult; A-F: Female adult. Data in the figure are mean±SD. Histograms with different letters indicate significant difference in the gene expression among different developmental stages at the 0.05 level by Duncan’s test. The same below.
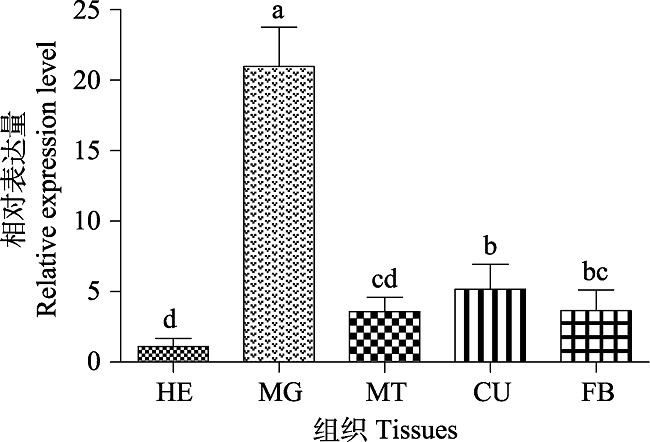
Fig. 8 Expression profiles of CpCPR in different tissues of fourth-instar Cydia pomonnella larvae HE: Head; CU: Cuticle; FB: Fat body; MG: Midgut; MT: Malpighian tubes.
| [1] |
Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T , 2006. The SWISS- MODEL workspace: A web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics, 22(2):195-201.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti770 URL pmid: 16301204 |
| [2] |
Balabanidou V, Kampouraki A, MacLean M, Blomquist GJ, Tittiger C, Juárez MP, Mijailovsky SJ, Chalepakis G, Anthousi A, Lynd A, Antoine S, Hemingway J, Ranson H, Lycett GJ, Vontas J , 2016. Cytochrome P450 associated with insecticide resistance catalyzes cuticular hydrocarbon production in Anopheles gambiae. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(33):9268-9273.
URL pmid: 27439866 |
| [3] |
Balabanidou V, Grigoraki L, Vontas J , 2018. Insect cuticle: A critical determinant of insecticide resistance. Current Opinion in Insect Science, 27:68-74.
URL pmid: 30025637 |
| [4] |
Bouvier JC, Boivin T, Beslay D, Sauphanor B , 2002. Age-dependent response to insecticides and enzymatic variation in susceptible and resistant codling moth larvae. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 51(2):55-66.
URL pmid: 12232873 |
| [5] |
Cheesman MJ, Traylor MJ, Hilton ME, Richards KE, Taylor MC, Daborn PJ, Russell RJ, Gillam EMJ, Oakeshott JG , 2013. Soluble and membrane-bound Drosophila melanogaster CYP6G1 expressed in E. coli: Purification, activity, and binding properties toward multiple pesticides. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 43(5):455-465.
doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2013.02.003 URL |
| [6] |
Chen X, Zhang Y , 2015. Identification and characterization of NADPH-dependent cytochrome P450 reductase gene and cytochrome b5 gene from Plutella xylostella: Possible involvement in resistance to beta-cypermethrin. Gene, 558(2):208-214.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.12.053 URL pmid: 25550052 |
| [7] |
Cheng J, Wan DF, Gu JR, Gong Y, Yang SL, Hao DC, Yang L , 2006. Establishment of a yeast system that stably expresses human cytochrome P450 reductase: Application for the study of drug metabolism of cytochrome P450s in vitro. Protein Expression and Purification, 47(2):467-476.
doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2005.11.022 URL pmid: 16434211 |
| [8] |
Eduardo FC, Reyes M, Barros W, Sauphanor B , 2007. Evaluation of azinphos-methyl resistance and activity of detoxifying enzymes in codling moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) from central Chile. Journal of Economic Entomology, 100(2):551-556.
doi: 10.1603/0022-0493(2007)100[551:eoaraa]2.0.co;2 URL pmid: 17461082 |
| [9] | Fang Y, Cai M, Ke X, Xing JC, Yang XQ, Wang XQ , 2018. Occurrence regularity of codling moth Cydia pomonella(Lepidoptera) on pear fruits in Zhangwu county of Liaoning province. Journal of Plant Protection, 45(4):724-730. |
| [ 房阳, 蔡明, 可欣, 邢竣策, 杨雪清, 王小奇 , 2018. 苹果蠹蛾在辽宁省彰武县梨树上的发生规律. 植物保护学报, 45(4):724-730.] | |
| [10] |
Feyereisen R , 1999. Insect P450 enzymes. Annual Review of Entomology, 44:507-533.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.ento.44.1.507 URL pmid: 9990722 |
| [11] |
Gillam EM , 2008. Engineering cytochrome P450 enzymes. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 21(1):220-223.
URL pmid: 18067267 |
| [12] |
He C, Liang JL, Liu SN, Zeng Y, Wang SL, Wu QJ, Xie W, Zhang YJ , 2020. Molecular characterization of an NADPH cytochrome P450 reductase from Bemisia tabaci Q: Potential involvement in susceptibility to imidacloprid. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 162:29-35.
doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2019.07.018 URL |
| [13] |
Ioriatti C, Tasin M, Charmillot PJ, Reyes M, Sauphanor B , 2007. Early detection of resistance to tebufenozide in field populations of Cydia pomonella L.: Methods and mechanisms. Journal of Applied Entomology, 131(7):453-459.
doi: 10.1111/jen.2007.131.issue-7 URL |
| [14] | Jin SJ , 2015. Occurrence and control of codling moth. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, ( 13):152. |
| [ 靳生杰 , 2015. 苹果蠹蛾的发生与防治. 现代农业科技, ( 13):152.] | |
| [15] | Kang XL , 2018. Functional study of cytochrome P450 reductase and cytochrome P450 genes in locust and corn borer. Master dissertation. Shanxi: Shanxi University. |
| [ 康晓林 , 2018. 飞蝗和玉米螟中细胞色素P450还原酶和细胞色素P450基因的功能研究. 硕士学位论文. 山西:山西大学.] | |
| [16] | Liang QM , 2014. RNAi study on the odorant binding proteins and NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase gene of Nilaparvata lugens. Mast dissertation. Zhejiang: Zhejiang Agricature University. |
| [ 梁庆梅 , 2014. 稻飞虱气味结合蛋白与P450还原酶的RNAi研究. 硕士学位论文. 浙江: 浙江大学.] | |
| [17] |
Liu S, Liang QM, Huang YJ, Huang YJ, Yuan X, Zhou WW, Qiao F, Cheng JA, Gurr GM, Zhu ZR , 2013. Cloning, functional characterization, and expression profiles of NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase gene from the Asiatic rice striped stem borer, Chilo suppressalis(Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology B-Biochemistry, 166(3/4):225-231.
doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2013.09.004 URL |
| [18] |
Lycett GJ, McLaughlin LA, Ranson H, Hemingway J, Kafatos FC, Loukeris TG, Paine MJI , 2006. Anopheles gambiae P450 reductase is highly expressed in oenocytes and in vivo knockdown increases permethrin susceptibility. Insect Molecular Biology, 15(3):321-327.
URL pmid: 16756551 |
| [19] | Paine MJI, Scrutton NS, Munro AW, Gutierrez A, Roberts GCK, Wolf CR , 2005. Electron Transfer Partners of Cytochrome P450. Boston: Springer. 115-148. |
| [20] |
Pasquier D, Charmillot PJ , 2003. Effectiveness of twelve insecticides applied topically to diapausing larvae of the codling moth, Cydia pomonella L. Pest Management Science, 60(3):305-308.
doi: 10.1002/ps.776 URL pmid: 15025243 |
| [21] |
Pittendrigh B, Aronstein K, Zinkovsky E, Andreev O, Campbell B, Daly J, Trowell S, Ffrench-Constant RH , 1997. Cytochrome P450 genes from Helicoverpa armigera: Expression in a pyrethroid-susceptible and-resistant strain. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 27(6):507-512.
doi: 10.1016/s0965-1748(97)00025-8 URL pmid: 9304792 |
| [22] | Pompon D , 1996. Yeast expression of animal and plant P450s in optimized redox environments. Methods Enzymol, 272(351):51-64. |
| [23] |
Reyes M, Frank P, Charmillot PJ, loriatti C, Olivares J, Pasqualini E, Sauphanor B , 2007. Diversity of insecticide resistance mechanisms and spectrum in European populations of codling moth, Cydia pomonella. Pest Management Science, 63(9):890-902.
doi: 10.1002/ps.1421 URL pmid: 17665366 |
| [24] |
Rodríguez MA, Marques T, Bosch D, Avilla J , 2011. Assessment of insecticide resistance in eggs and neonate larvae of Cydia pomonella(Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 100(2):151-159.
doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2011.03.003 URL |
| [25] |
Rose R, Goh D, Thompson DM, Verma KD, Heckle DG, Gahan LJ, Roe RM, Hodgson E , 1997. Cytochrome P450 (CYP)9A1 in Heliothis virescens: The first member of a new CYP family. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 27(6):605-615.
URL pmid: 9304798 |
| [26] |
Sauphanor B, Bouvier JC, Brosse V , 1998. Spectrum of insecticide resistance in Cydia pomonella(Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in Southeastern France. Journal of Economic Entomology, 91(6):1225-1231.
doi: 10.1093/jee/91.6.1225 URL |
| [27] |
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S , 2013. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6. 0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30(12):2725-2729.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst197 URL |
| [28] |
Tang T, Zhao C, Feng X, Liu X, Qiu L, Tang T, Zhao C, Feng X, Liu XY, Qiu LH , 2012. Knockdown of several components of cytochrome P450 enzyme systems by RNA interference enhances the susceptibility of Helicoverpa armigera to fenvalerate. Pest Management Science, 68(11):1501-1511.
doi: 10.1002/ps.3336 URL pmid: 22689565 |
| [29] |
Voudouris CC, Sauphanor B, Frank P, Reyes M, Mamuris Z, Tsitsipis JA, Vontas J, Margaritopoulos JT , 2011. Insecticide resistance status of the codling moth Cydia pomonella(Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) from Greece. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 100(3):229-238.
doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2011.04.006 URL |
| [30] |
Wan FH, Yin C, Tang R, Chen MH, Wu Q, Huang C, Qian WQ, Stabelli O, Yang NW, Wang SP, Wang GR, Zhang GF, Guo JY, Gu LQ, Chen LF, Xing LS, Xi Y, Liu FL, Lin KJ, Guo MB, Liu W, He K, Tian RZ, Joly E, Franck P, Siegwart M, Ometto L, Anfora G, Blaxter M, Meslin C, Nguyen P, Dalíková M, Marec F, Olivares J, Maugin S, Shen JR, Liu JD, Guo JM, Luo JP, Liu B, Fan W, Feng LK, Zhao XX, Peng X, Wang K, Liu L, Zhan HX, Liu WX, Shi GL, Jiang CY, Jin JS, Xian XQ, Lu S, Ye ML, Li MZ, Yang ML, Xiong RC, Walters J, Li F , 2019. A chromosome-level genome assembly of Cydia pomonella provides insights into chemical ecology and insecticide resistance. Nature Communications, 10(1):1-14.
URL pmid: 30602773 |
| [31] | Wang D , 2011. Cloning, spatiotemporal expression and RNA interference of NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase gene in Helicoverpa armigera. Master dissertation. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricature University. |
| [ 汪丹 , 2011. 棉铃虫NADPH-细胞色素P450还原酶基因的克隆、时空表达及RNA干扰. 硕士学位论文. 南京: 南京农业大学.] | |
| [32] | Xu J, Liu W, Liu H, Wu LF, Zhang RZ , 2015. Spread and harm of codling moth in China. Journal of Biosafety, 24(4):327-336. |
| [ 徐婧, 刘伟, 刘慧, 吴立峰, 张润志 , 2015. 苹果蠹蛾在中国的扩散与危害. 生物安全学报, 24(4):327-336.] | |
| [33] |
Yang XQ, Wang W, Tan XL, Wang XQ, Dong H , 2017. Comparative analysis of recombinant cytochrome P450 CYP9A61 from Cydia pomonella expressed in Escherichia coli and Pichia pastoris. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65(11):2337-2344.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00372 URL pmid: 28271709 |
| [34] | Yang XQ, Zhang YL , 2014. Molecular cloning, sequence analysis and mRNA expression stability detection of β-actin gene in codling moth Cydia pomonella (L.). Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 42(11):135-140. |
| [ 杨雪清, 张雅林 , 2014. 苹果蠹蛾β-actin基因cDNA的克隆、序列分析及mRNA表达稳定性检测. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 42(11):135-140.] | |
| [35] | Yang XQ , 2014. Molecular cloning and function study of detoxifying genes from Cydia pomonella (L.). Doctoral dissertation. Yangling: Northwest A&F University. |
| [ 杨雪清 , 2014. 苹果蠹蛾解毒酶基因克隆及功能研究. 博士学位论文. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.] | |
| [36] | Yu H, Liu S, Zhu QZ, Zhou WW, Liang QM, Shi XX, Zhu ZJ, Zhu ZR , 2016. Molecular characteristics and expression analysis of cytochrome P450 reductase gene in Sogatella furcifera. Journal of Zhejiang University(Agriculture & Life Sciences), 42(4):391-400. |
| [ 余航, 刘苏, 朱晴子, 周文武, 梁庆梅, 史肖肖, 祝梓杰, 祝增荣 , 2016. 白背飞虱细胞色素P450还原酶基因的分子特征与表达模式分析. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 42(4):391-400.] | |
| [37] | Zhao CQ , 2014. Cloning, heterologous co-expression and effects on different compounds on the GABA receptor of Helicoverpa armigera cytochrome P450 enzyme related genes. Doctoral dissertation. Beijing: China Agricultural University. |
| [ 赵春青 , 2014. 棉铃虫细胞色素P450酶系相关基因克隆、异源共表达及不同化合物对GABA受体结合作用影响研究. 博士学位论文. 北京: 中国农业大学.] | |
| [38] | Zhang HB , 2018. Monitoring and control of codling moth in Qinzhou District, Tianshui City. Agricultural Science-Technology and Information, ( 16):56-57. |
| [ 张鸿斌 , 2018. 天水市秦州区苹果蠹蛾监测与防控. 农业科技与信息, ( 16):56-57.] | |
| [39] | Zhang XZ, Zhou SL, Wang YJ , 1958. A preliminary study on the codling moth. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 8(2):136-150. |
| [ 张学祖, 周绍来, 王庸俭 , 1958. 苹果蠹蛾的初步研究. 昆虫学报, 8(2):136-150.] | |
| [40] |
Zhang XY, Wang JX, Liu J, Li YH, Liu XJ, Wu HH, Ma EB, Zhang ZB , 2017. Knockdown of NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase increases the susceptibility to carbaryl in the migratory locust, Locusta migratoria. Chemosphere, 188:517-524.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.157 URL pmid: 28910726 |
| [41] |
Zhu F, Sams S, Moural T, Haynes KF, Potter MF, Palli SR , 2012. RNA interference of NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase results in reduced insecticide resistance in the bed bug, Cimex lectularius. PLoS ONE, 7(2):e31037.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031037 URL pmid: 22347424 |
| [1] | Teng-Fei SHI, An-Ran WANG, Yu-Jie ZHU, Lin-Sheng YU. Sublethal effects of sulfoxaflor on the expression of detoxification, immune and memory related, genes in the honeybee (Apis mellifera ligustica) [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2020, 57(4): 833-840. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
