Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology ›› 2020, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 889-897.doi: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2020.091
• Research Articles • Previous Articles
Xia-Hui OUYANG***( ), Shuai PENG(
), Shuai PENG( ), Wen-Kai XU, Xue-Lei ZHU, Xiang-Xiang ZHENG, Hong CHEN
), Wen-Kai XU, Xue-Lei ZHU, Xiang-Xiang ZHENG, Hong CHEN
Received:2019-07-18
Accepted:2019-08-05
Online:2020-07-27
Published:2020-09-02
Contact:
Xia-Hui OUYANG
E-mail:oyxhui316@126.com;1609409157@qq.com
Xia-Hui OUYANG, Shuai PENG, Wen-Kai XU, Xue-Lei ZHU, Xiang-Xiang ZHENG, Hong CHEN. Cloning, sequence characterization and expression of the Apis mellifera amPGAM2 gene[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2020, 57(4): 889-897.
| 引物 Primers | 引物序列(5¢-3¢) Primer sequence (5¢-3¢) | 引物用途 Use of primers |
|---|---|---|
| PGAM2-F | AATACGATAGGTGGTGGGGG | 扩增引物 Amplified primers |
| PGAM2-R | TGAAACACATCTCTAGAAAAACATC | |
| q-pgam2(s) | TCCGATAAAGGTAAGATTGAAGCA | 实时荧光定量PCR RT-qPCR |
| q-pgam2(a) | ACGTTCATTTAATCGCCATGTCTTT | |
| qβ-actin-2F | TGCCAACACTGTCCTTTCTG | |
| qβ-actin-2R | AGAATTGACCCACCAATCCA |
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| 引物 Primers | 引物序列(5¢-3¢) Primer sequence (5¢-3¢) | 引物用途 Use of primers |
|---|---|---|
| PGAM2-F | AATACGATAGGTGGTGGGGG | 扩增引物 Amplified primers |
| PGAM2-R | TGAAACACATCTCTAGAAAAACATC | |
| q-pgam2(s) | TCCGATAAAGGTAAGATTGAAGCA | 实时荧光定量PCR RT-qPCR |
| q-pgam2(a) | ACGTTCATTTAATCGCCATGTCTTT | |
| qβ-actin-2F | TGCCAACACTGTCCTTTCTG | |
| qβ-actin-2R | AGAATTGACCCACCAATCCA |
| 蛋白质理化特性 Physicochemical properties of proteins | 预测结果 Prediction results |
|---|---|
| 分子式Molecular formula | C1306H2050N350O380S8 |
| 等电点Isoelectric point | 7.07 |
| 负电荷氨基酸残疾总数(Asp + Glu)Total disability of negatively charged amino acids (Asp + Glu) | 35 |
| 正电荷氨基酸残疾总数(Arg + Lys)Total disability of positive charge amino acids (Arg + Lys) | 35 |
| 不稳定指数Instability index | 39.24 |
| 总平均亲水性系数Total average hydrophilicity coefficient | ﹣0.505 |
| 半衰期Half life | 30 h |
Table 2 Physicochemical properties of amPGAM2 in Apis mellifera
| 蛋白质理化特性 Physicochemical properties of proteins | 预测结果 Prediction results |
|---|---|
| 分子式Molecular formula | C1306H2050N350O380S8 |
| 等电点Isoelectric point | 7.07 |
| 负电荷氨基酸残疾总数(Asp + Glu)Total disability of negatively charged amino acids (Asp + Glu) | 35 |
| 正电荷氨基酸残疾总数(Arg + Lys)Total disability of positive charge amino acids (Arg + Lys) | 35 |
| 不稳定指数Instability index | 39.24 |
| 总平均亲水性系数Total average hydrophilicity coefficient | ﹣0.505 |
| 半衰期Half life | 30 h |
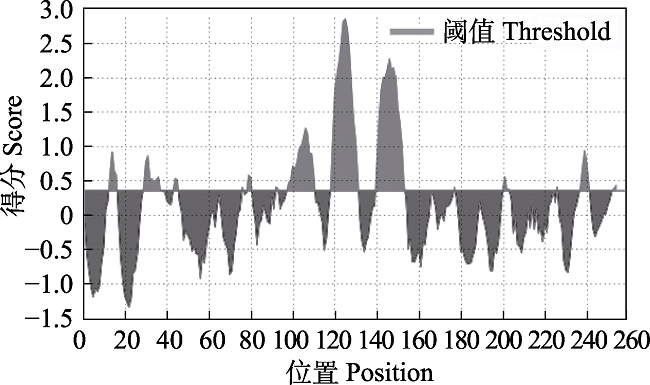
Fig. 4 Analysis of B cell antigen epitopes of amPGAM2 protein in Apis mellifera The transverse axis is the amino acid sequence of protein and the longitudinal axis is the antigen index. The peak interval above the critical value is the potential antigen epitope.
| 顺序 Order | 氨基酸位置 Amino acid position | 潜在抗原表位序列 Potential epitope sequence | 得分 Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13-16 | ESEW | 0.915 |
| 2 | 29-38 | HLSDKGKIEA | 0.860 |
| 3 | 43-45 | KAI | 0.530 |
| 4 | 76 | Q | 0.400 |
| 5 | 79-80 | IT | 0.580 |
| 6 | 92-93 | YG | 0.403 |
| 7 | 98-110 | LNKAETAAKYGEE | 1.259 |
| 8 | 118-131 | SFDTPPPPMEPDHK | 2.850 |
| 9 | 140-153 | PRYANDPKPEEFPK | 2.269 |
| 10 | 166 | P | 0.350 |
| 11 | 177 | K | 0.404 |
| 12 | 200-203 | EMSN | 0.556 |
| 13 | 224 | N | 0.353 |
| 14 | 226 | K | 0.406 |
| 15 | 237-241 | EETVK | 0.935 |
Table 3 Potential antigenic epitopes in the amino acid sequence of amPGAM2 in Apis mellifera
| 顺序 Order | 氨基酸位置 Amino acid position | 潜在抗原表位序列 Potential epitope sequence | 得分 Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13-16 | ESEW | 0.915 |
| 2 | 29-38 | HLSDKGKIEA | 0.860 |
| 3 | 43-45 | KAI | 0.530 |
| 4 | 76 | Q | 0.400 |
| 5 | 79-80 | IT | 0.580 |
| 6 | 92-93 | YG | 0.403 |
| 7 | 98-110 | LNKAETAAKYGEE | 1.259 |
| 8 | 118-131 | SFDTPPPPMEPDHK | 2.850 |
| 9 | 140-153 | PRYANDPKPEEFPK | 2.269 |
| 10 | 166 | P | 0.350 |
| 11 | 177 | K | 0.404 |
| 12 | 200-203 | EMSN | 0.556 |
| 13 | 224 | N | 0.353 |
| 14 | 226 | K | 0.406 |
| 15 | 237-241 | EETVK | 0.935 |

Fig. 5 Expression of amPGAM2 gene in different grades and developmental stages of Apis mellifera G-2: Egg stage of worker bees 2 days old; G-3: Egg stage of worker bees 3 days old; G-5: Larval stage of worker bees 5 days old; G-7: Larval stage of worker bees 7 days old; G-9: Larval stage of worker bees 9 days old; G-11: Larval stage of worker bees 11 days old; G-Y: Worker bees prepupa; G-B: Worker bees white eye pupa; G-H: Worker bees red eye pupa; G-C: Worker bees adult. X-2: Egg stage of drones 2 days old; X-3: Egg stage of drones 3 days old ; X-4: Larva stage of drones 4 years old; X-6: Larva stage of drones 6 years old; X-8: Larva stage of drones 8 years old; X-10: Larva stage of drones 10 years old; X-12: Larva stage of drones 12 years old; X-Y: Drones prepupa; X-B: Drones white eye pupa; X-H: Drones red eye pupa; X-C: Drones adult. W-2: Egg stage of queen bees 2 days old; W-3: Egg stage of Queen bees 3 days old; W-4: Larva stage of queen bees 4 days old; W-5: Larva stage of queen bees 5 days old; W-6: Larva stage of queen bees 6 days old; W-7: Larva stage of queen bees 7 days old; W-Y: Queen bees pre-pupa; W-B: Queen bees white eye pupa; W-H: Queen bees red eye pupa; W-C: Queen bees adult. Histograms with different letters indicate significant difference in variance analysis of single factors (P <0.05, Duncan’s multiple comparison).
| [1] |
Castellà-Escolà J, Montoliu L, Pons G, Puigdomènech P, Cohen-Solal M, Carreras J, Rigau J, Climent F , 1989. Sequence of rat skeletal muscle phosphoglycerate mutase cDNA. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 165(3):1345-1351.
doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92751-4 URL pmid: 2558656 |
| [2] |
Delom F, Chevet E , 2006. Phosphoprotein analysis: From proteins to proteomes. Proteome Science, 4:15.
doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-4-15 URL pmid: 16854217 |
| [3] |
DiMauro S, Miranda AF, Khan S, Gitlin K, Friedman R , 1981. Human muscle phosphoglycerate mutase deficiency: Newly discovered metabolic myopathy. Science, 212(4500):1277-1279.
doi: 10.1126/science.6262916 URL pmid: 6262916 |
| [4] |
Ferramosca A, Zara V , 2014. Bioenergetics of mammalian sperm capacitation. BioMed Research International, 2014: 902953.
doi: 10.1155/2014/902953 URL pmid: 24791005 |
| [5] | Fothergill LA, Harkins RN , 1982. The amino acid sequence of yeast phosphoglycerate mutase. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 215(1198):19-44. |
| [6] |
Gizak A, Grenda M, Mamczur P, Wisniewski J, Sucharski F, Silberring J, McCubrey JA, Wisniewski JR, Rakus D , 2015. Insulin/IGF1-PI3K-dependent nucleolar localization of a glycolytic enzyme--phosphoglycerate mutase 2, is necessary for proper structure of nucleolus and RNA synthesis. Oncotarget, 6(19):17237-17250.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4044 URL pmid: 26033454 |
| [7] |
Guruprasad K, Reddy BV, Pandit MW , 1990. Correlation between stability of a protein and its dipeptide composition: A novel approach for predicting in vivo stability of a protein from its primary sequence. Protein Engineering, 4(2):155-161.
doi: 10.1093/protein/4.2.155 URL pmid: 2075190 |
| [8] |
Garavelli JS , 2004. The RESID database of protein modifications as a resource and annotation tool. Proteomics, 4(6):1527-1533.
doi: 10.1002/pmic.200300777 URL pmid: 15174122 |
| [9] |
Hannaert V, Brinkmann H, Nowitzki U, Lee JA, Albert MA, Sensen CW, Gaasterland T, Müller M, Michels P, Martin W , 2000. Enolase from Trypanosoma brucei, from the amitochondriate protist Mastigamoeba balamuthi, and from the chloroplast and cytosol of Euglena gracilis: Pieces in the evolutionary puzzle of the eukaryotic glycolytic pathway. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 17(7):989-1000.
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026395 URL pmid: 10889212 |
| [10] |
Hereng TH, Elgstoen KB, Cederkvist FH, Eide L, Jahnsen T, Skålhegg BS, Rosendal KR , 2011. Exogenous pyruvate accelerates glycolysis and promotes capacitation in human spermatozoa. Human Reproduction, 26(12):3249-3263.
doi: 10.1093/humrep/der317 URL pmid: 21946930 |
| [11] |
Hadjigeorgiou GM, Kawashima N, Bruno C, Andreu AL, Sue CM, Rigden DJ, Kawashima A, Shanske S, DiMauro S , 1999. Manifesting heterozygotes in a Japanese family with a novel mutation in the muscle-specific phosphoglycerate mutase (PGAM-M) gene. Neuromuscul Disord, 9(6/7):399-402.
doi: 10.1016/S0960-8966(99)00039-5 URL |
| [12] |
Krisher RL, Prather RS , 2012. A role for the warburg effect in preimplantation embryo development: Metabolic modification to support rapid cell proliferation. Molecular Reproduction & Development, 79(5):311-320.
doi: 10.1002/mrd.22037 URL pmid: 22431437 |
| [13] |
Kondoh H, Lleonart ME, Gil J, Wang J, Degan P, Peters G, Martinez D, Carnero A, Beach D , 2005. Glycolytic enzymes can modulate cellular life span. Cancer Research, 65(1):177-185.
URL pmid: 15665293 |
| [14] | Li QZ, Zhu GQ, Liu WX, Liu LX, Zhang L , 2016. Bioinformatics analysis of CDS of TLR6 gene in Holstein cattle. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 32(3):608-614. |
| [ 李强子, 朱国强, 刘吴鑫, 刘丽霞, 张丽 , 2016. 荷斯坦牛TLR6基因CDS区的生物信息学分析. 江苏农业学报, 32(3):608-614.] | |
| [15] | Lu YB, Wan Y, Wu YZ , 2003. Prediction of the secondary structure and B cell epitope for the E protein of SARS coronavirus. Immunological Journal, ( 6):407-410. |
| [ 吕燕波, 万瑛, 吴玉章 , 2003. SARS病毒基因组所编码的E蛋白的二级结构和B细胞表位预测. 免疫学杂志, ( 6):407-410.] | |
| [16] |
Liu F, Gong ZH, Zhang WX, Wang Y, Ma LT, Wang HF, Guo XQ, Xu BH , 2015. Identification and characterization of a novel methionine sulfoxide reductase B gene (AccMsrB) from Apis cerana cerana(Hymenoptera: Apidae). Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 108(4):575-584.
doi: 10.1093/aesa/sav042 URL |
| [17] |
Li Q, Miao DQ, Zhou P, Wu YG, Gao D, Wei DL, Cui W, Tan JH , 2011. Glucose metabolism in mouse cumulus cells prevents oocyte aging by maintaining both energy supply and the intracellular redox potential. Biology of Reproduction, 84(6):1111-1118.
URL pmid: 21270427 |
| [18] |
Oh SJ, Park KS, Ryan HF Jr, Danon MJ, Lu J, Naini AB, DiMauro S , 2006. Exercise-induced cramp, myoglobinuria, and tubular aggregates in phosphoglycerate mutase deficiency. Muscle & Nerve, 34(5):572-576.
doi: 10.1002/mus.20622 URL pmid: 16881065 |
| [19] |
Okomo-Adhiambo M, Beattie C, Rink A , 2006. cDNA microarray analysis of host-pathogen interactions in a porcine in vitro model for Toxoplasma gondii infection. Infection and Immunity, 74(7):4254-4265.
URL pmid: 16790800 |
| [20] |
Qiu HF, Zhao SH, Xu XW, Yerle M, Liu B , 2008. Assignment and expression patterns of porcine muscle-specific isoform of phosphoglycerate mutase gene. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 35(5):257-260.
doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(08)60036-3 URL |
| [21] |
Ruiz-Lozano P, de Lecea L, Buesa C, Pérez de la Osa P, LePage D, Gualberto A, Walsh K, Pons G , 1994. The gene encoding rat phosphoglycerate mutase subunit M: Cloning and promoter analysis in skeletal muscle cells. Gene, 147(2):243-248.
doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90074-4 URL pmid: 7926808 |
| [22] | Sun XN , 2016. Toxoplasma gondⅡ: The cloning and expression of enzymes related with energy metabolism and functional regulation study of mouse macrophages. Master dissertation. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University. |
| [ 孙晓妮 , 2016. 刚地弓形虫4种能量代谢相关酶基因的克隆表达及对小鼠巨噬细胞功能的调节. 硕士学位论文. 南京: 南京农业大学.] | |
| [23] |
Sakoda S, Shanske S, Dimauro S, DiMauro EA , 1988. Isolation of a cDNA encoding the B isozyme of human phosphoglycerate mutase (PGAM) and characterization of the PGAM family. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 263(32):16899-16905.
URL pmid: 2846553 |
| [24] |
Shanske S, Sakoda S, Hermodson MA, DiMauro S, Schon EA , 1987. Isolation of a cDNA encoding the muscle-specific subunit of human phosphoglycerate mutase. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 262(30):14612-14617.
URL pmid: 2822696 |
| [25] | Szpirer C, Szpirer J, Van Vooren P, Tissir F, Simon JS, Koike G, Jacob HJ, Lander ES, Helou K, Klinga-Levan K, Levan G , 1999. Gene-based anchoring of the rat genetic linkage and cytogenetic maps. Transplantation Proceedings, 31(3):1541-1543. |
| [26] |
Su YQ, Sugiura K, Eppig JJ , 2009. Mouse oocyte control of granulosa cell development and function: Paracrine regulation of cumulus cell metabolism. Seminars in Reproductive Medicine, 27(1):32-42.
URL pmid: 19197803 |
| [27] |
Tennessen JM, Baker KD, Lam G, Evans J, Thummel CS , 2011. The drosophila estrogen-related receptor directs a metabolic switch that supports developmental growth. Cell Metabolism, 13(2):139-148.
URL pmid: 21284981 |
| [28] |
Turhani D, Krapfenbauer K, Thurnher D, Langen H, Fountoulakis M , 2006. Identification of differentially expressed, tumor-associated proteins in oral squamous cell carcinoma by proteomic analysis. Electrophoresis, 27(7):1417-1423.
doi: 10.1002/elps.200500510 URL pmid: 16568407 |
| [29] | Wu XX, Tang ZL, Li Y, Yang SL, Chu MX, Ma YH, Li K , 2008. Cloning, Sequence characteristics and expression analysis of PGAM2 gene. Chinese Journal of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 35(5):1183-1189. |
| [ 伍晓雄, 唐中林, 李勇, 杨述林, 储明星, 马月辉, 李奎 , 2008. 猪PGAM2基因的克隆、序列特征及表达分析. 畜牧兽医学报, 39(9):1183-1189.] | |
| [30] |
Woods IG, Wilson C, Friedlander B, Chang P, Reyes DK, Nix R, Kelly PD, Chu F, Postlethwait JH, Talbot WS , 2005. The zebrafish gene map defines ancestral vertebrate chromosomes. Genome Research, 15(9):1307-1314.
doi: 10.1101/gr.4134305 URL pmid: 16109975 |
| [31] | Wu ZL , 2015. Effect of MSTN, Ankrd2 on cell differentiation of SCs and association analysis of PGAM2, XKR4 polymorphisms on growth traits in rabbits. Master dissertation. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University. |
| [ 吴周林 , 2015. 兔MSTN, Ankrd2对骨骼肌卫星细胞分化影响及PGAM2, XKR4基因与家兔生长性状关联分析. 硕士学位论文. 成都: 四川农业大学.] | |
| [32] | Wang F , 2011. Bioinformatics analysis, cloning, expression of PGAM2 gene of Toxoplasma gondii and immunoprotection of rTgPGAM2. Master dissertation. Taiyuan: Shanxi Medical University. |
| [ 王芬 , 2011. 刚地弓形虫磷酸甘油酸变位酶2基因的生物信息学分析、克隆表达及免疫保护性研究. 硕士学位论文. 太原: 山西医科大学.] | |
| [33] | Wang YB , 2011. Effects of glycometabolism during maturation on the cytoplasm of goat oocytes. Master dissertation. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University. |
| [ 王彦博 , 2011. 山羊卵母细胞成熟期间葡萄糖代谢作用对卵母细胞胞质成熟的影响. 硕士学位论文. 泰安: 山东农业大学.] | |
| [34] | Xu YS, Chen L, Wang N, Zang CY, Peng FK, Zhang J , 2019. Inhibition of glycolysis activity limits the proliferation of male primordial germ cells. Progress in Modern Biomedicine, 19(10):1823-1828. |
| [ 徐瑜珊, 陈丽, 王娜, 臧春燕, 彭凡珂, 张军 , 2019. 抑制糖酵解活性限制雄性原始生殖细胞的增殖. 现代生物医学进展, 19(10):1823-1828.] | |
| [35] |
Zhang J, Yu L, Fu Q, Gao J, Xie Y, Chen J, Zhang P, Liu Q, Zhao S , 2001. Mouse phosphoglycerate mutase M and B isozymes: cDNA cloning, enzyme activity assay and mapping. Gene, 264(2):273-279.
doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(00)00597-7 URL pmid: 11250083 |
| [36] |
Zhao Z, Assmann SM , 2011. The glycolytic enzyme, phosphoglycerate mutase, has critical roles in stomatal movement, vegetative growth, and pollen production in Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Experimental Botany, 62(14):5179-5189.
URL pmid: 21813794 |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
