Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology ›› 2020, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 980-987.doi: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2020.101
• Research Articles • Previous Articles
Peng-Liang PAN1,2( ), Feng HONG1,2, Jun-Hua CHEN1,2, Hong-Min LIU1,2, Xin-Ming YIN3,***(
), Feng HONG1,2, Jun-Hua CHEN1,2, Hong-Min LIU1,2, Xin-Ming YIN3,***( ), Jian-Wei XIONG1,2
), Jian-Wei XIONG1,2
Received:2019-03-15
Accepted:2019-07-23
Online:2020-07-27
Published:2020-09-02
Contact:
Xin-Ming YIN
E-mail:panpl@xyafu.edu.cn;xinmingyin@hotmail.com
Peng-Liang PAN, Feng HONG, Jun-Hua CHEN, Hong-Min LIU, Xin-Ming YIN, Jian-Wei XIONG. Extraction and analysis of numerical characteristics from forewings of three plant hopper species (Homoptera: Ricaniidae)[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2020, 57(4): 980-987.
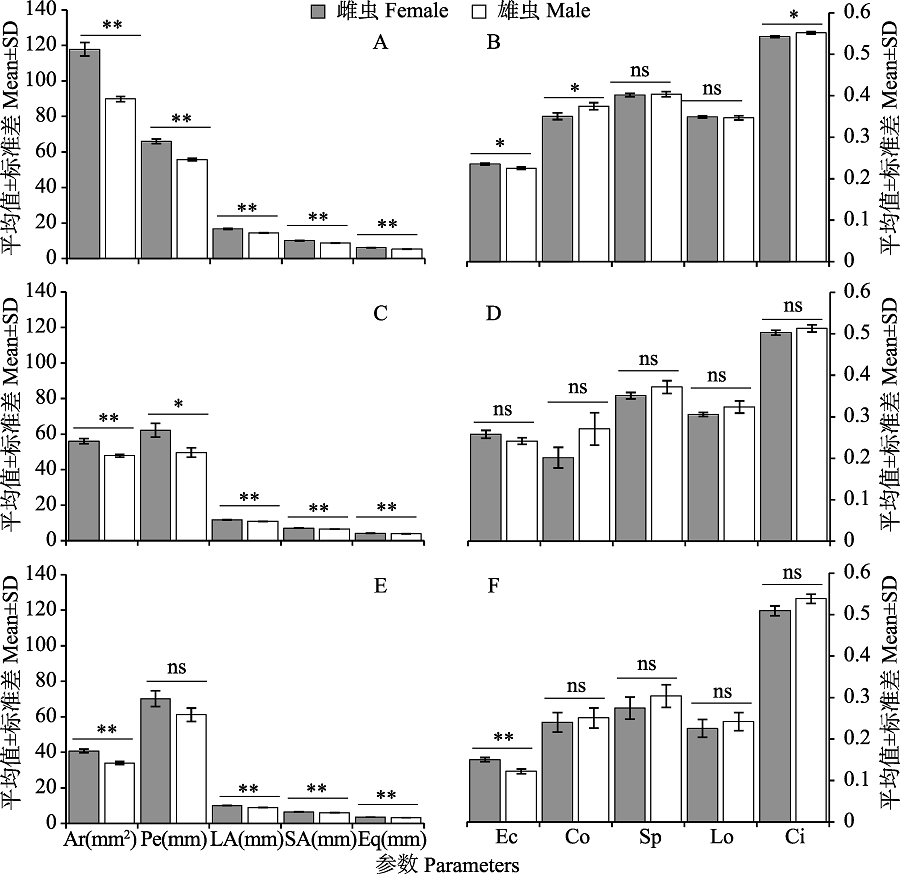
Fig. 2 Comparison results of morphological parameters about forewings of male and female from three plant hopper species A, B. R. sublimbata; C, D. R. spechlum; E, F. E. clara. The data in the figure are mean±SD; ** indicates significantly different at 0.01 level, * indicates significantly different at 0.05 level, and the ns indicates no significant difference between different sexual samples in one species. Ar: Area; Pe: Perimeter; LA: Long axis; SA: Short axis; Eq: Equal radius; Ec: Eccentricity; Co: Compactness; Sp: Sphericity; Lo: Lobation; Ci: Circlularity.
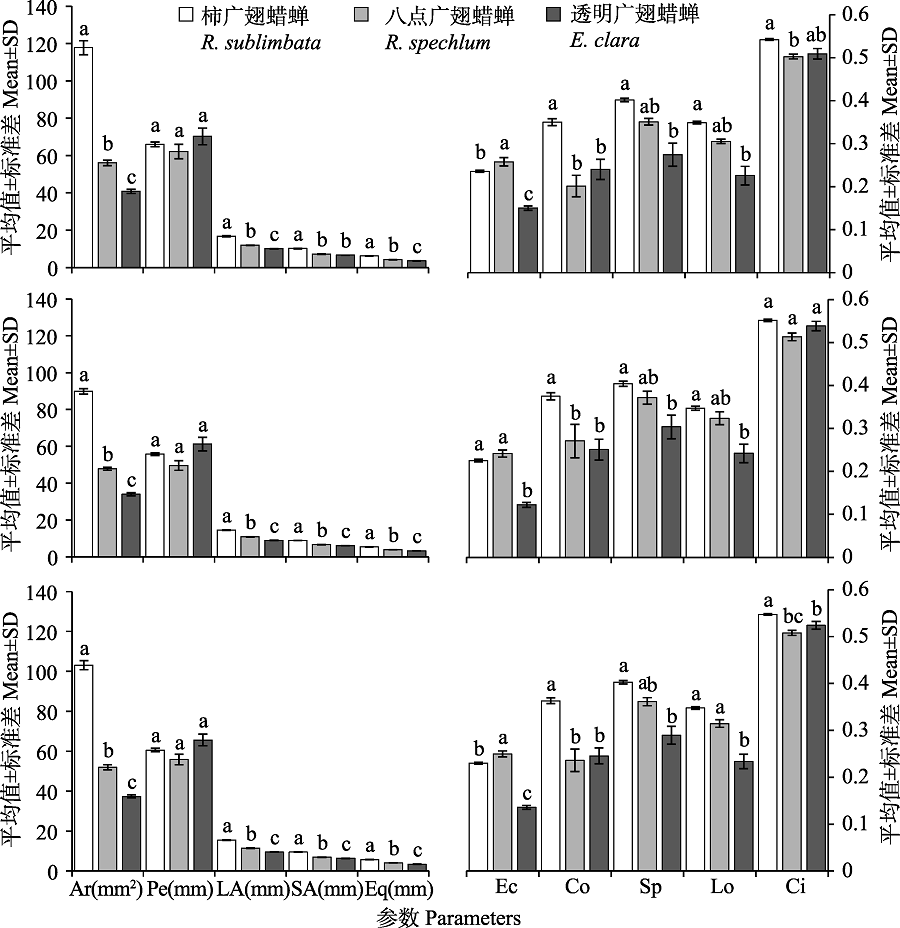
Fig. 3 Difference of morphological parameters of forewings from three plant hopper species with different data sets The data in the figure are mean±SD. Histograms with different letters within one group indicate significant difference between species, while same letters indicate no significant difference at 0.05 level. Ar: Area; Pe: Perimeter; LA: Long axis; SA: Short axis; Eq: Equal radius; Ec: Eccentricity; Co: Compactness; Sp: Sphericity; Lo: Lobation; Ci: Circlularity.
| 数据类型 Data types | 种类 Species | 预测组成员(%)Predicted group membership (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | |||
| 综合数据a1,c1 Aggregate data | 原始 Original | 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 98.6 | 0.0 | 1.4 |
| 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 0.0 | 95.0 | 5.0 | ||
| 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | 0.0 | 0.7 | 99.3 | ||
| 交叉验证b Cross-validated | 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 98.6 | 0.0 | 1.4 | |
| 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 5.0 | 90.0 | 5.0 | ||
| 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | 0.0 | 0.7 | 99.3 | ||
| 实际测量数据a2,c2 Direct measurement data | 原始 Original | 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 98.6 | 0.0 | 1.4 |
| 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 10.0 | 80.0 | 10.0 | ||
| 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | 0.0 | 0.7 | 99.3 | ||
| 交叉验证b Cross-validated | 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 98.6 | 0.0 | 1.4 | |
| 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 10.0 | 80.0 | 10.0 | ||
| 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | 0.0 | 0.7 | 99.3 | ||
| 二次数据a3,c3 Secondary data | 原始 Original | 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 97.8 | 0.0 | 2.2 |
| 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 55.0 | 40.0 | 5.0 | ||
| 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | 8.0 | 0.7 | 91.3 | ||
| 交叉验证b Cross-validated | 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 97.8 | 0.0 | 2.2 | |
| 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 65.0 | 30.0 | 5.0 | ||
| 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | 8.0 | 0.7 | 91.3 | ||
Table 1 Results of canonical discriminant analysis about different data sets from three plant hopper species
| 数据类型 Data types | 种类 Species | 预测组成员(%)Predicted group membership (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | |||
| 综合数据a1,c1 Aggregate data | 原始 Original | 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 98.6 | 0.0 | 1.4 |
| 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 0.0 | 95.0 | 5.0 | ||
| 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | 0.0 | 0.7 | 99.3 | ||
| 交叉验证b Cross-validated | 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 98.6 | 0.0 | 1.4 | |
| 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 5.0 | 90.0 | 5.0 | ||
| 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | 0.0 | 0.7 | 99.3 | ||
| 实际测量数据a2,c2 Direct measurement data | 原始 Original | 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 98.6 | 0.0 | 1.4 |
| 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 10.0 | 80.0 | 10.0 | ||
| 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | 0.0 | 0.7 | 99.3 | ||
| 交叉验证b Cross-validated | 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 98.6 | 0.0 | 1.4 | |
| 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 10.0 | 80.0 | 10.0 | ||
| 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | 0.0 | 0.7 | 99.3 | ||
| 二次数据a3,c3 Secondary data | 原始 Original | 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 97.8 | 0.0 | 2.2 |
| 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 55.0 | 40.0 | 5.0 | ||
| 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | 8.0 | 0.7 | 91.3 | ||
| 交叉验证b Cross-validated | 柿广翅蜡蝉 R. sublimbata | 97.8 | 0.0 | 2.2 | |
| 八点广翅蜡蝉 R. spechlum | 65.0 | 30.0 | 5.0 | ||
| 透明广翅蜡蝉 E. clara | 8.0 | 0.7 | 91.3 | ||
| [1] |
Chang XL, Zhai BP, Liu XD, Wang M , 2007. Effects of temperature stress and pesticide exposure on fluctuating asymmetry and mortality of Copera annulata (Selys) (Odonata: Zygoptera) larvae. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 67(1):120-127.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.04.004 URL |
| [2] | Deng LM, Wang YJ, Han ZZ, Yu RS , 2018. Research on insect pest image detection and recognition based on bio-inspired methods. Biosystems Engineering, ( 169):139-148. |
| [3] |
Joan DC, Elisa RM, Sebastià JR, Sergio MN, Anna S, Samuel P , 2018. Individual unique colour patterns of the pronotum of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus(Coleoptera: Curculionidae) allow for photographic identification methods (PIM). Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 21(2):519-526.
doi: 10.1016/j.aspen.2018.03.002 URL |
| [4] |
Jose B, Juan GS, Abelardo G, Patricia C, Rafael A, Enrique M , 2008. Automatic sex detection of individuals of Ceratitis capitata by means of computer vision in a biofactory. Pest Management Science, 65(1):99-104.
doi: 10.1002/ps.1652 URL pmid: 18823066 |
| [5] |
Kalafi EY, Town C, Dhillon SK , 2018. How automated image analysis techniques help scientists in species identification and classification? Folia Morphologica, 77(2):179-193.
URL pmid: 28868609 |
| [6] | Leonard RJ, Wat KKY, McArthur C, Hochuli DF , 2018. Urbanisation and wing asymmetry in the western honey bee ( Apis mellifera Linnaeus, 1758) at multiple scales. Peer J., ( 12):e5940. |
| [7] | Nattero J, Cecere MC, Gürtler RE , 2017. Temporal variations of fluctuating asymmetry in wing size and shape of Triatoma infestans populations from northwest Argentina. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, ( 56):133-142. |
| [8] | Nawrocka A, Kandemir İ, Fuchs S, Tofilski A , 2018. Computer software for identification of honey bee subspecies and evolutionary lineages. Apidologie, 49(2):172-184. |
| [9] | Pan PL, Shi HZ, Yin XM , 2017. Application of insect mathematical morphology in gender recognition of peach longicorn beetle (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 46(12):159-164. |
| [ 潘鹏亮, 史洪中, 尹新明 , 2017. 昆虫数学形态学在桃红颈天牛雌雄成虫鉴别中的应用. 河南农业科学, 46(12):159-164.] | |
| [10] |
Perrard A, Baylac M, Carpenter JM, Villemant C , 2014. Evolution of wing shape in hornets: Why is the wing venation efficient for species identification? Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 27(12):2665-2675.
doi: 10.1111/jeb.12523 URL |
| [11] | Rohlf FJ , 2015. The tps series of software. Hystrix, 26(1):9-12. |
| [12] | Shen ZR, Yu XW , 1998. Perspective and research of mathematical insect morphology and its application. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 41(S1):142-150. |
| [ 沈佐锐, 于新文 , 1998. 昆虫数学形态学研究及其应用展望. 昆虫学报, 41(增刊):142-150.] | |
| [13] | Tan JC , 1995. Investigation on fulgorid planthoppers (Fulgoridae) in tea gardens of Hunan province. Journal of Tea Science, 15(1):33-37. |
| [ 谭济才 , 1995. 湖南省茶园蜡蝉种类调查研究初报. 茶叶科学, 15(1):33-37.] | |
| [14] |
Tofilski A , 2004. DrawWing, a program for numerical description of insect wings. Journal of Insect Science, 17(4):1-5.
doi: 10.1093/jisesa/iew097 URL |
| [15] |
Vakilian KA, Massah J , 2013. Performance evaluation of a machine vision system for insect pests identification of field crops using artificial neural networks. Archives of Phytopathology and Plant Protection, 46(11):1262-1269.
doi: 10.1080/03235408.2013.763620 URL |
| [16] | Weng GR , 2008. Monitoring population density of pests based on mathematical morphology. Transactions of the CSAE, 24(11):135-138. |
| [ 翁桂荣 , 2008. 数学形态学在害虫种群密度监测中的应用. 农业工程学报, 24(11):135-138.] | |
| [17] | Xu P, Chen NZ, Yang D , 2010. Automatic identification of insects. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology, 47(2):256-262. |
| [ 徐鹏, 陈乃中, 杨定 , 2010. 自动识别技术在昆虫分类鉴别研究中的应用. 昆虫知识, 47(2):256-262.] | |
| [18] |
Yang HP, Ma CS, Wen H, Zhang QB, Wang XL , 2015. A tool for developing an automatic insect identification system based on wing outlines. Scientific Reports , doi: 10.1038/srep12786.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70536-7 URL pmid: 32859928 |
| [19] | Yang HZ, Shen ZR, Li XT , 2011. Advances on automatic insect identification. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 30(5):834-838. |
| [ 杨红珍, 沈佐锐, 李湘涛 , 2011. 昆虫自动鉴定技术研究与展望. 四川动物, 30(5):834-838.] | |
| [20] | Yu SQ, Xu AZ, Wang RZ , 2018. A preliminary study on the host plants of Ricania sublimbata Jacobi. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 24(23):55-56. |
| [ 俞素琴, 徐爱珍, 汪荣灶 , 2018. 柿广翅蜡蝉寄主植物的初步研究. 安徽农学通报, 24(23):55-56.] | |
| [21] | Yu XW, Shen ZR, Gao LW, Li ZH , 2003. Feature measuring and extraction for digital image of insects. Journal of China Agricultural University, 8(3):47-50. |
| [ 于新文, 沈佐锐, 高灵旺, 李志红 , 2003. 昆虫图像几何形状特征的提取技术研究. 中国农业大学学报, 8(3):47-50.] | |
| [22] | Zhao FH, Lü LZ, Ren HL , 2010. Plant hoppers: A new pest insect found in Xinyang area. China Tea, 32(10):16-17. |
| [ 赵丰华, 吕立哲, 任红楼 , 2010. 信阳茶树新害虫——蜡蝉. 中国茶叶, 32(10):16-17.] | |
| [23] | Zhao FH, Lü LZ, Ren HL, Gong FP, Jiang SF, Dang YC , 2011. Biological characteristics of Ricania sublimbata from tea plantations in the Southern Henan province. China Tea, 33(5):18-19. |
| [ 赵丰华, 吕立哲, 任红楼, 龚凤萍, 蒋双丰, 党永超 , 2011. 豫南茶园柿广翅蜡蝉生物学特性. 中国茶叶, 33(5):18-19.] | |
| [24] | Zhou Y, Lu JS , 1977. On the Chinese Ricaniidae with descriptions of eight new species. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 20(3):314-322. |
| [ 周尧, 路进生 , 1977. 中国的广翅蜡蝉科附八新种. 昆虫学报, 20(3):314-322.] |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
