应用昆虫学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 898-910.doi: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2020.092
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2019-11-11
接受日期:2020-02-12
出版日期:2020-07-27
发布日期:2020-09-02
通讯作者:
刘乃勇
E-mail:1835949501@qq.com;Naiyong_2013@163.com
基金资助:
Zheng-Quan WANG( ), Ning-Na YIN, Ning ZHAO, Nai-Yong LIU***(
), Ning-Na YIN, Ning ZHAO, Nai-Yong LIU***( )
)
Received:2019-11-11
Accepted:2020-02-12
Online:2020-07-27
Published:2020-09-02
Contact:
Nai-Yong LIU
E-mail:1835949501@qq.com;Naiyong_2013@163.com
摘要:
【目的】 昆虫UDP-葡萄糖基转移酶(UGT)在其内源性和外源性有毒化合物的解毒代谢过程中起着重要作用,但在管纹艳虎天牛Rhaphuma horsfieldi中UGT基因的研究尚属空白。【方法】 采用转录组学、生物信息学、进化和表达谱分析、蛋白同源建模等技术研究了管纹艳虎天牛的UGT基因家族。【结果】 从管纹艳虎天牛转录组中一共鉴定到36个RhorUGTs基因,其中17个具有全长序列。鞘翅目不同种间UGT基因数量的比较表明,管纹艳虎天牛具有中等数量的UGT基因。进化分析结果表明,RhorUGTs分布在10个亚家族中,其中UGT352亚家族为天牛科昆虫所特有,且该亚家族中RhorUGT2/7/10/16/18/27可能通过基因的复制产生。表达谱结果表明,大部分RhorUGTs基因在检测的所有组织中均有表达,部分基因呈现触角或跗节特异或高表达的特点,暗示它们具有嗅觉或触觉等功能。三级结构分析发现,RhorUGT17的α3、α4、β4和β5主要参与UDP-葡萄糖的结合。【结论】 本研究明确了管纹艳虎天牛UGT基因的数量、序列特征、进化关系及组织表达特征,研究结果为该种天牛解毒代谢机制的阐明奠定基础。
王政全, 尹宁娜, 赵宁, 刘乃勇. 管纹艳虎天牛UDP-葡萄糖基转移酶基因的鉴定及表达特征分析 *[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2020, 57(4): 898-910.
Zheng-Quan WANG, Ning-Na YIN, Ning ZHAO, Nai-Yong LIU. Identification and expression characterization of UDP-glucosyltransferase genes in Rhaphuma horsfieldi[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2020, 57(4): 898-910.

图1 管纹艳虎天牛UGT的氨基酸序列比对 三角形表示起催化作用的组氨酸(H)和天冬氨酸(D);1、2和3分别表示与核苷酸、含磷化合物和糖苷作用的氨基酸。
Fig. 1 Multiple alignment of UGT amino acid sequences in Rhaphuma horsfieldi Triangle represents key catalytic residues (H, histidine and D, aspartic acid). 1, 2 and 3 represent nucleotide, phosphate and glucoside interacting residues, respectively.
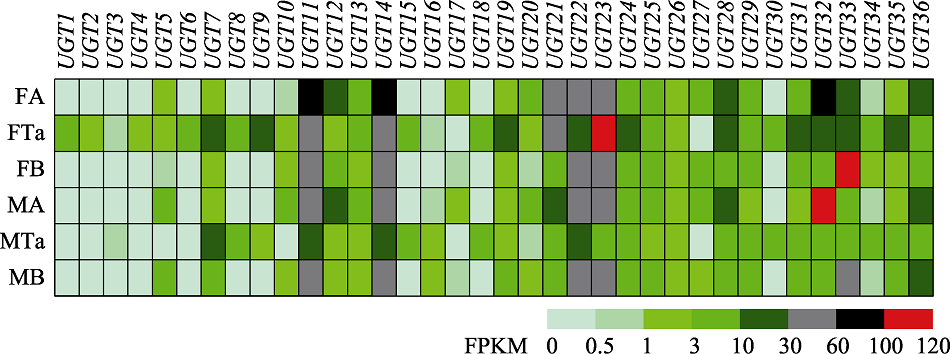
图3 管纹艳虎天牛RhorUGTs基因在成虫不同组织的表达谱 FA:成虫触角;FTa:雌虫跗节;FB:不含触角和跗节的身体;MA:雄虫触角;MTa:雄虫跗节;MB:不含触角和跗节的身体。
Fig. 3 Expression pattern of RhorUGT genes in different tissues of Rhaphuma horsfieldi adults FA: Female antennae; FTa: Female tarsi; FB: Female bodies without antennae and tarsi; MA: Male antennae; MTa: Male tarsi; MB: Male bodies without antennae and tarsi.
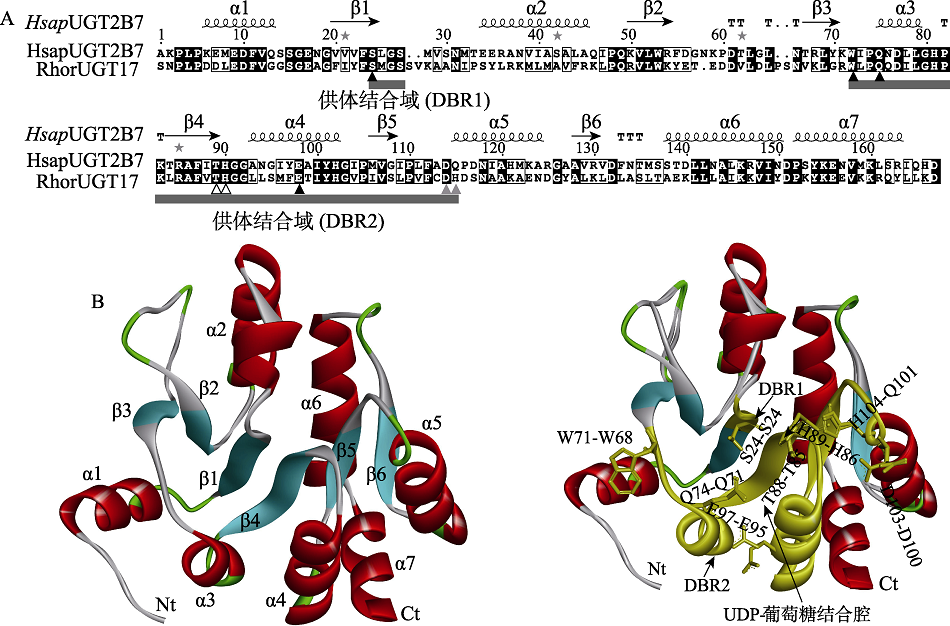
图4 管纹艳虎天牛RhorUGT17的三级结构 A. 管纹艳虎天牛RhorUGT17与人HsapUGT2B7的氨基酸序列比对;B. 管纹艳虎天牛RhorUGT17的三级结构(左边)及其与HsapUGT2B7的三级结构叠加(右边)。两个蛋白的关键氨基酸(S、W、Q、T、H、E、D和H/Q)和UDP-葡萄糖结合腔在结构中被标示;供体结合区域(DBR1和DBR2)用黄色标示;Nt、Ct、α1-7和β1-6:分别表示氨基酸端、羧基端、α螺旋1至7和β折叠1至6。
Fig. 4 Three-dimensional (3D) structure of Rhaphuma horsfieldi UGT17 A. Alignment of RhorUGT17 and HsapUGT2B7 amino acid sequences; B. 3D model of RhorUGT17 (left) and superimposition of RhorUGT17 and HsapUGT2B7 structures (right). Key residues (S, W, Q, T, H, E, D and H/Q) and UDP-glucose binding cavities of RhorUGT17 and HsapUGT2B7 are labeled on the structures, respectively. Donor binding domains (DBR1 and DBR2) are highlighted in yellow. Nt, Ct, α1-7 and β1-6 represent N-terminus, C-terminus, seven α-helixes and six β-sheets, respectively.
| [1] |
Ahn SJ, Vogel H, Heckel DG , 2012. Comparative analysis of the UDP-glycosyltransferase multigene family in insects. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol., 42(2):133-147.
doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2011.11.006 URL |
| [2] |
Betz O , 2003. Structure of the tarsi in some Stenus species (Coleoptera, Staphylinidae): External morphology, ultrastructure, and tarsal secretion. J. Morphol., 255(1):24-43.
doi: 10.1002/jmor.10044 URL pmid: 12420319 |
| [3] |
Bock KW , 2016. The UDP-glycosyltransferase (UGT) superfamily expressed in humans, insects and plants: Animal-plant arms-race and co-evolution. Biochem. Pharmacol., 99:11-17.
doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.10.001 URL |
| [4] |
Bozzolan F, Siaussat D, Maria A, Durand N, Pottier MA, Chertemps T, Maibeche-Coisne M , 2014. Antennal uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glycosyltransferases in a pest insect: Diversity and putative function in odorant and xenobiotics clearance. Insect Mol. Biol., 23(5):539-549.
doi: 10.1111/imb.2014.23.issue-5 URL |
| [5] | Evans JD, McKenna D, Scully E, Cook SC, Dainat B, Egekwu N, Grubbs N, Lopez D, Lorenzen MD, Reyna SM, Rinkevich FD, Neumann P, Huang Q , 2018. Genome of the small hive beetle (Aethina tumida, Coleoptera: Nitidulidae), a worldwide parasite of social bee colonies, provides insights into detoxification and herbivory. GigaScience, 7(12):1-16. |
| [6] | Forestry Department of Yunnan Province, Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1987. Yunnan Forest Insects. Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Publishing Press. 665. |
| [ 云南省林业厅, 中国科学院动物研究所, 1987. 云南森林昆虫. 昆明: 云南科技出版社. 665.] | |
| [7] |
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O , 2010. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3. 0. Syst. Biol., 59(3):307-321.
doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syq010 URL pmid: 20525638 |
| [8] |
He P, Zhang YF, Hong DY, Wang J, Wang XL, Zuo LH, Tang XF, Xu WM, He M , 2017. A reference gene set for sex pheromone biosynthesis and degradation genes from the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella, based on genome and transcriptome digital gene expression analyses. BMC Genomics, 18(1):219.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3592-y URL pmid: 28249567 |
| [9] |
Hu B, Zhang S, Ren M, Tian X, Wei Q, Mburu DK, Su J , 2019. The expression of Spodoptera exigua P450 and UGT genes: Tissue specificity and response to insecticides. Insect Sci., 26(2):199-216.
doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12538 URL pmid: 28881445 |
| [10] |
Huang FF, Chai CL, Zhang Z, Liu ZH, Dai FY, Lu C, Xiang ZH , 2008. The UDP-glucosyltransferase multigene family in Bombyx mori. BMC Genomics, 9:563.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-563 URL pmid: 19038024 |
| [11] | Huang FF, Liu ZH, Chen YH, Ma Y, Lu C , 2009. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of UDP-glucosyltransferase gene BmUGT004965 in Bombyx mori. Science of Sericulture, 35(1):50-57. |
| [ 黄飞飞, 刘增虎, 陈颜虹, 马艳, 鲁成 , 2009. 家蚕尿苷二磷酸-葡萄糖基转移酶基因(BmUGT004965)的克隆和表达谱分析. 蚕业科学, 35(1):50-57.] | |
| [12] | Ji SS, Liu NY, Zhao N, Zhuang XL , 2017. Characteristic differences of male and female adults of Xylotrechus rufilius. Forest Pest and Disease, 36(4):29-33. |
| [ 吉帅帅, 刘乃勇, 赵宁, 庄翔麟 , 2017. 白蜡脊虎天牛雌雄成虫特征差异. 中国森林病虫, 36(4):29-33.] | |
| [13] | Jiang SN, Pu FJ, Hua LZ , 1985. Economic Entomology of China (Volume 35: Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Beijing: Science Press. 84. |
| [ 蒋书南, 蒲富基, 华立中 , 1985. 中国经济昆虫志(第35 册: 鞘翅目: 天牛科). 北京: 科学出版社. 84.] | |
| [14] |
Kaplanoglu E, Chapman P, Scott IM, Donly C , 2017. Overexpression of a cytochrome P450 and a UDP- glycosyltransferase is associated with imidacloprid resistance in the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata. Sci. Rep., 7(1):1762.
URL pmid: 28496260 |
| [15] |
Katoh K, Standley DM , 2013. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol., 30(4):772-780.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst010 URL |
| [16] |
Keeling CI, Yuen MM, Liao NY, Docking TR, Chan SK, Taylor GA, Palmquist DL, Jackman SD, Nguyen A, Li M, Henderson H, Janes JK, Zhao Y, Pandoh P, Moore R, Sperling FA, Huber DP, Birol I, Jones SJ, Bohlmann J , 2013. Draft genome of the mountain pine beetle, Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins, a major forest pest. Genome Biol., 14(3):R27.
URL pmid: 23537049 |
| [17] |
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG , 2007. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2. 0. Bioinformatics, 23(21):2947-2948.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404 URL pmid: 17846036 |
| [18] | Lou LL , 2014. Effect of pesticides on UDP-glycosyltransferases activity in Spodoptera litura. Master dissertation. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University. |
| [ 娄琳琳 , 2014. 杀虫剂对斜纹夜蛾UDP-葡萄糖基转移酶活性的影响. 硕士学位论文. 南京: 南京农业大学.] | |
| [19] |
Mackenzie PI, Owens IS, Burchell B, Bock KW, Bairoch A, Belanger A, Fournel-Gigleux S, Green M, Hum DW, Iyanagi T, Lancet D, Louisot P, Magdalou J, Chowdhury JR, Ritter JK, Schachter H, Tephly TR, Tipton KF, Nebert DW , 1997. The UDP glycosyltransferase gene superfamily: Recommended nomenclature update based on evolutionary divergence. Pharmacogenetics, 7(4):255-269.
doi: 10.1097/00008571-199708000-00001 URL pmid: 9295054 |
| [20] |
McKenna DD, Scully ED, Pauchet Y, Hoover K, Kirsch R, Geib SM, Mitchell RF, Waterhouse RM, Ahn SJ, Arsala D, Benoit JB, Blackmon H, Bledsoe T, Bowsher JH, Busch A, Calla B, Chao H, Childers AK, Childers C, Clarke DJ, Cohen L, Demuth JP, Dinh H, Doddapaneni H, Dolan A, Duan JJ, Dugan S, Friedrich M, Glastad KM, Goodisman MA, Haddad S, Han Y, Hughes DS, Ioannidis P, Johnston JS, Jones JW, Kuhn LA, Lance DR, Lee CY, Lee SL, Lin H, Lynch JA, Moczek AP, Murali SC, Muzny DM, Nelson DR, Palli SR, Panfilio KA, Pers D, Poelchau MF, Quan H, Qu J, Ray AM, Rinehart JP, Robertson HM, Roehrdanz R, Rosendale AJ, Shin S, Silva C, Torson AS, Jentzsch IM, Werren JH, Worley KC, Yocum G, Zdobnov EM, Gibbs RA, Richards S , 2016. Genome of the Asian longhorned beetle ( Anoplophora glabripennis), a globally significant invasive species, reveals key functional and evolutionary innovations at the beetle-plant interface. Genome Biol., 17(1):227.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-1088-8 URL pmid: 27832824 |
| [21] | Meech R, Mackenzie PI , 1997. Structure and function of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferases. Clin. Exp. Pharanacol. Physiol., 24(12):907-915. |
| [22] |
Meyer JM, Markov GV, Baskaran P, Herrmann M, Sommer RJ, Rödelsperger C , 2016. Draft genome of the scarab beetle Oryctes borbonicus on La Réunion Island. Genome Biol. Evol., 8(7):2093-2105.
doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw133 URL pmid: 27289092 |
| [23] |
Miley MJ, Zielinska AK, Keenan JE, Bratton SM, Radominska- Pandya A, Redinbo MR , 2007. Crystal structure of the cofactor-binding domain of the human phase II drug-metabolism enzyme UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 2B7. J. Mol. Biol., 369(2):498-511.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.03.066 URL pmid: 17442341 |
| [24] |
Osmani SA, Bak S, Moller BL , 2009. Substrate specificity of plant UDP-dependent glycosyltransferases predicted from crystal structures and homology modeling. Phytochemistry, 70(3):325-347.
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.12.009 URL |
| [25] |
Pearce SL, Clarke DF, East PD, Elfekih S, Gordon KHJ, Jermiin LS, McGaughran A, Oakeshott JG, Papanikolaou A, Perera OP, Rane RV, Richards S, Tay WT, Walsh TK, Anderson A, Anderson CJ, Asgari S, Board PG, Bretschneider A, Campbell PM, Chertemps T, Christeller JT, Coppin CW, Downes SJ, Duan G, Farnsworth CA, Good RT, Han LB, Han YC, Hatje K, Horne I, Huang YP, Hughes DST, Jacquin-Joly E, James W, Jhangiani S, Kollmar M, Kuwar SS, Li S, Liu NY, Maibeche MT, Miller JR, Montagne N, Perry T, Qu J, Song SV, Sutton GG, Vogel H, Walenz BP, Xu W, Zhang HJ, Zou Z, Batterham P, Edwards OR, Feyereisen R, Gibbs RA, Heckel DG, McGrath A, Robin C, Scherer SE, Worley KC, Wu YD , 2017. Genomic innovations, transcriptional plasticity and gene loss underlying the evolution and divergence of two highly polyphagous and invasive Helicoverpa pest species. BMC Biol., 15:63.
doi: 10.1186/s12915-017-0402-6 URL pmid: 28756777 |
| [26] |
Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H , 2011. SignalP 4. 0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods, 8(10):785-786.
URL pmid: 21959131 |
| [27] |
Sali A, Blundell TL , 1993. Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J. Mol. Biol., 234(3):779-815.
doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1626 URL |
| [28] |
Trapnell C, Williams B, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van BMJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L , 2010. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol., 28(5):511-515.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.1621 URL pmid: 20436464 |
| [29] |
Wang Q, Hasan G, Pikielny CW , 1999. Preferential expression of biotransformation enzymes in the olfactory organs of Drosophila melanogaster, the antennae. J. Biol. Chem., 274(15):10309-10315.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.15.10309 URL pmid: 10187818 |
| [30] |
Wang S, Liu Y, Zhou JJ, Yi JK, Pan Y, Wang J, Zhang XX, Wang JX, Yang S, Xi JH , 2018. Identification and tissue expression profiling of candidate UDP-glycosyltransferase genes expressed in Holotrichia parallela motschulsky antennae. Bull. Entomol. Res., 108(6):807-816.
doi: 10.1017/S0007485318000068 URL pmid: 29397056 |
| [31] |
Wickhamm JD, Harrison RD, Lu W, Guo Z, Millar JG, Hanks LM, Chen Y , 2014. Generic lures attract cerambycid beetles in a tropical montane rain forest in southern China. J. Econ. Entomol., 107(1):259-267.
doi: 10.1603/EC13333 URL |
| [32] |
Wu Z, Bin S, He H, Wang Z, Li M, Lin J , 2016. Differential expression analysis of chemoreception genes in the striped flea beetle Phyllotreta striolata using a transcriptomic approach. PLoS ONE, 11(4):e0153067.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153067 URL pmid: 27064483 |
| [33] | Yin NN, Zhao N, Liu NY , 2019. Morphological characteristics of Rhaphuma horsfieldi and ultrastructure of its antennae and tarsi. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Sciences), 39(3):132-140. |
| [ 尹宁娜, 赵宁, 刘乃勇 , 2019. 管纹艳虎天牛形态特征与触角及跗节的超微结构. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 39(3):132-140.] | |
| [34] |
Younus F, Chertemps T, Pearce SL, Pandey G, Bozzolan F, Coppin CW, Russell RJ, MaibecheCoisne M, Oakeshott JG , 2014. Identification of candidate odorant degrading gene/enzyme systems in the antennal transcriptome of Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol., 53:30-43.
doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2014.07.003 URL pmid: 25038463 |
| [35] | Zhang SH , 2016. The effect of insecticide on expression levels of UDP-glycosyltransferase in Spodoptera exigua. Master dissertation. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University. |
| [ 张书恒 , 2016. 杀虫剂处理对甜菜夜蛾尿苷二磷酸葡萄糖基转移酶基因表达的影响. 硕士学位论文. 南京: 南京农业大学.] | |
| [36] |
Zhang YN, Ma JF, Xu L, Dong ZP, Xu JW, Li MY, Zhu XY , 2017. Identification and expression patterns of UDP- glycosyltransferase (UGT) genes from insect pest Athetis lepigone(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol., 20(1):253-259.
doi: 10.1016/j.aspen.2017.01.008 URL |
| [1] | 王传鹏, 张帅, 高雪珂, 雒珺瑜, 朱香镇, 王丽, 张开心, 杨亦桦, 崔金杰. 三个棉蚜谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶(GST)基因克隆及在不同寄主专化型中的表达分析 *[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2020, 57(4): 823-832. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
