Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology ›› 2020, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 841-849.doi: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2020.086
• Special Column • Previous Articles
Dan-Yang GUAN1( ), Xiao-Wei JIANG1, Qing-Ya LI1, Xiao LIU1, Yong-Qiang MA2, Qiang CHEN1, Hongmei LI-Byarlay3, Bing-Jun HE1,***(
), Xiao-Wei JIANG1, Qing-Ya LI1, Xiao LIU1, Yong-Qiang MA2, Qiang CHEN1, Hongmei LI-Byarlay3, Bing-Jun HE1,***( )
)
Received:2020-01-10
Accepted:2020-04-09
Online:2020-07-27
Published:2020-09-02
Contact:
Bing-Jun HE
E-mail:dy13512892573@163.com;hebj@nankai.edu.cn
Dan-Yang GUAN, Xiao-Wei JIANG, Qing-Ya LI, Xiao LIU, Yong-Qiang MA, Qiang CHEN, Hongmei LI-Byarlay, Bing-Jun HE. Effects of Guadipyr on voltage-gated calcium and potassium channels in central neurons of Helicoverpa armigera[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2020, 57(4): 841-849.
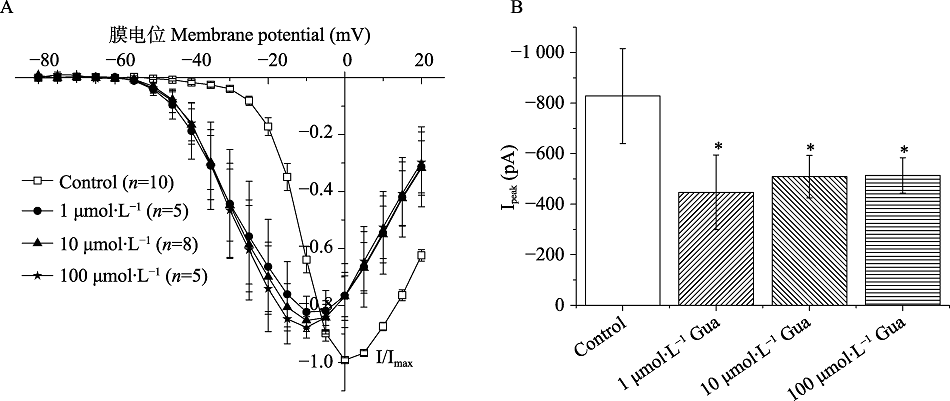
Fig. 2 TheⅠ-Ⅴcurves and Ipeak of Ca2+ channels before and after the application of Gua A. Gua's effects on the Ⅰ-Ⅴ curve of Ca2+ channels: Standardized current amplitude; B. The Ipeak of Ca2+ channels after Gua. * indicats significant difference compared with the control (P<0.05, One-way analysis of variance). The same as Fig.7.
| 条件 Condition | 激活 Activation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| V0.5a | kb | n | |
| 对照 Control | –9.83±0.73 | 4.55±0.38 | 10 |
| 1 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 1 μmol?L–1 Gua | –22.85±5.02* | 5.27±0.26 | 5 |
| 10 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 10 μmol?L–1 Gua | –23.45±3.36* | 5.48±0.21 | 8 |
| 100 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 100 μmol?L–1 Gua | –24.21±3.74* | 5.46±0.26 | 5 |
Table 1 Effects of Gua on the steady-state activation of ICa
| 条件 Condition | 激活 Activation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| V0.5a | kb | n | |
| 对照 Control | –9.83±0.73 | 4.55±0.38 | 10 |
| 1 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 1 μmol?L–1 Gua | –22.85±5.02* | 5.27±0.26 | 5 |
| 10 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 10 μmol?L–1 Gua | –23.45±3.36* | 5.48±0.21 | 8 |
| 100 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 100 μmol?L–1 Gua | –24.21±3.74* | 5.46±0.26 | 5 |
| 条件 Condition | 失活 Inactivation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| V0.5a | kb | n | |
| 对照 Control | –22.30±2.46 | 18.45±3.60 | 7 |
| 1 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 1 μmol?L–1 Gua | –26.26±2.86 | 13.58±3.36 | 5 |
| 10 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 10 μmol?L–1 Gua | –24.76±2.44 | 12.28±2.95 | 6 |
| 100 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 100 μmol?L–1 Gua | –28.69±3.12 | 13.41±3.13 | 5 |
Table 2 Effects of Gua on the steady-state inactivation of ICa
| 条件 Condition | 失活 Inactivation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| V0.5a | kb | n | |
| 对照 Control | –22.30±2.46 | 18.45±3.60 | 7 |
| 1 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 1 μmol?L–1 Gua | –26.26±2.86 | 13.58±3.36 | 5 |
| 10 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 10 μmol?L–1 Gua | –24.76±2.44 | 12.28±2.95 | 6 |
| 100 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 100 μmol?L–1 Gua | –28.69±3.12 | 13.41±3.13 | 5 |

Fig. 7 TheⅠ-Ⅴ curves and Ipeak of IK before and after the application of Gua A. Gua’s effects on the I-V curve of K+ channels: Current amplitude is not standardized; B. The Ipeak of K+ channels after Gua.
| 条件 Condition | 激活 Activation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| V0.5a | kb | n | |
| 对照Control | 22.15±1.72 | 21.10±0.74 | 13 |
| 10 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 10 μmol?L–1 Gua | 31.72±1.07* | 22.31±0.78 | 7 |
| 100 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 100 μmol?L–1 Gua | 29.35±1.55 | 24.16±1.93 | 4 |
Table 3 Effects of Gua on the steady-state activation of IK
| 条件 Condition | 激活 Activation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| V0.5a | kb | n | |
| 对照Control | 22.15±1.72 | 21.10±0.74 | 13 |
| 10 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 10 μmol?L–1 Gua | 31.72±1.07* | 22.31±0.78 | 7 |
| 100 μmol?L–1戊吡虫胍 100 μmol?L–1 Gua | 29.35±1.55 | 24.16±1.93 | 4 |
| [1] | Ahmad M, Gladwell RT, McCaffery AR , 1989. Decreased nerve sensitivity is a mechanism of resistance in a pyrethroid resistant strain of Heliothis armigera from Thailand. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 35(2):165-171. |
| [2] | Ahmad M, McCaffery AR , 1991. Elucidation of detoxication mechansims involved in resistance to insecticides in the third instar larvae of field-selected strain of Helicoverpa armigera with the use of synergists. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 41(1):41-52. |
| [3] |
Bloomquist JR , 1996. Ion channels as targets for insecticides. Annual Review of Entomology, 41:163-190.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.41.010196.001115 URL pmid: 8546445 |
| [4] |
Cao Z, Shafer TJ, Murray TF , 2010. Mechanisms of pyrethroid insecticide-induced stimulation of calcium influx in neocortical neurons. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 336(1):197-205.
doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.171850 URL pmid: 20881019 |
| [5] |
Clark JM, Symington SB , 2007. Pyrethroid action on calcium channels: Neurotoxicological implications. Invertebrate Neuroscience, 7(1):3-6.
URL pmid: 17294162 |
| [6] |
Hamill OF, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ , 1981. Improved patch clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Archiv European Journal of Physiology, 391(2):85-100.
URL pmid: 6270629 |
| [7] | He BJ, Chen JT, Guo SY, Rui HH, Meng XQ, Wang XL, Wang YN, Sun JS, Liu AX , 2001. Nerve cell culture and ultrastrucal analysis of central nerve genglia from resistant Helicoverpa armigera. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Nankaiensis, 34(1):30-36. |
| [ 贺秉军, 陈家童, 郭世宜, 芮黄辉, 孟香清, 王秀玲, 王亦农, 孙金生, 刘安西 , 2001. 抗性棉铃虫神经细胞的离体培养和超微结构分析. 南开大学学报, 34(1):30-36.] | |
| [8] | He BJ, Liu AX, Chen JT, Sun JS, Rui CH , 2002. Study on the mechanism of action of cyhalothrin on sodium and calcium channels of nerve cells from Helicoverpa armigera. Acta Biophysica Sinica, 18(2):201-205. |
| [ 贺秉军, 刘安西, 陈家童, 孙金生, 芮昌辉 , 2002. 三氟氯氰菊酯对棉铃虫神经细胞钠及钙通道作用机理研究. 生物物理学报, 18(2):201-205.] | |
| [9] | He XW, Yin RY, Chen YH, LV J, Xie ZP, He FS , 1997. Effect of pyrethroids on Na+、Ca2+ channel currents in rat brain neurons. Chinese Journal of Industrial Hygiene and Occupational Diseases, 15(5):261-264. |
| [ 贺锡文, 殷若元, 陈寅红, 吕京, 谢佐平, 何凤生 , 1997. 拟除虫菊酯对神经细胞膜Na+、Ca2+离子通道的影响. 中华劳动卫生职业病杂志, 15(5):261-264.] | |
| [10] | Li DZ, Wang K, Xu L, Chai TT, Cui F, Qiu LH, Zheng MQ, Qin ZH, Wang CJ , 2006. Acute toxicity of guadipyr to non-target organisms. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 11(3):331-337. |
| [ 李冬植, 王凯, 徐莉, 柴婷婷, 崔峰, 邱立红, 郑明奇, 覃兆海, 王成菊 , 2006. 戊吡虫胍对几种非靶标生物的急性毒性. 生态毒理学报, 11(3):331-337.] | |
| [11] | Liu AX, Chen ST , 1990. Modified action of cypermethrin enantiomers on axonal sodium and potassium channels of Periplaneta Fulginosa(Serville). Acta Entomologica Sinica, 33(1):1-6. |
| [ 刘安西, 陈守同 , 1990. 氯氰菊酯异构体对黑胸大蠊神经钠钾通道的调制作用. 昆虫学报, 33(1):1-6.] | |
| [12] |
Neal AP, Yuan Y, Atchison WD , 2010. Allethrin differentially modulates voltage-gated calcium channel subtypes in rat PC12 cells. Toxicological Sciences, 116(2):604-613.
doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq139 URL pmid: 20466778 |
| [13] |
Nishimura K, Kanda Y, Okazawa A, Ueno T , 1994. Relationship between insecticidal and neyrophysiological activities of imidacloprid and related compounds. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 50(1):51-59.
doi: 10.1006/pest.1994.1057 URL |
| [14] |
Qi SZ, Wang C, Chen XF, Qin ZH, Li XF, Wang CJ , 2013. Toxicity assessments with Daphnia magna of Guadipyr, a new neonicotinoid insecticide and studies of its effect on acetylcholinesterase (AChE), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), catalase (CAT) and chitobiase activities. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, doi.org/ 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.09.013.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111192 URL pmid: 32858326 |
| [15] |
Rao GV, Rao KS , 1997. Modulation of K+ transport across synaptosomes of rat brain by synthetic pyrethroids . Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 147(2):127-133.
doi: 10.1016/s0022-510x(96)05327-0 URL pmid: 9106117 |
| [16] |
Salgado VL , 1992. The neurotoxic insecticidal mechanism of the nonsterodial ecdysone agonist RH-5849: K+ channel block in nerve and muscle. Pestic Biochem. Physiol., 43(1):1-13.
doi: 10.1016/0048-3575(92)90013-P URL |
| [17] | Shang XL , 2014. Effects of tefluthrin and deltamethrin on calcium channels and BK channels in central neurons isolated from Helicoverpa armigera. Master dissertation. Tianjin: Nankai University. |
| [ 商学良 , 2014. 七氟菊酯和溴氰菊酯对棉铃虫神经细胞Ca 2+通道及Ca 2+激活K +通道(BK)作用机理的研究 . 硕士学位论文. 天津: 南开大学.] | |
| [18] | Sheng CF, Xuan WJ, Su JW, Wang HT , 2001. A protracted disaster of cotton bollworm in China and the role of sex pheromone in the disaster reduction. Journal of Natural Disasters, 10(1):75-79. |
| [ 盛承发, 宣维健, 苏建伟, 王红托 , 2001. 棉铃虫灾害的长期性及性信息素的减灾控害作用. 自然灾害学报, 10(1):75-79.] | |
| [19] |
Soderlund DM, Clark JM, Sheets L P, Mullin LS, Piccirillo VJ, Sargent D, Stevens JT, Weiner ML , 2001. Mechanisms of pyrethroid neurotoxicity: Implications for cumulative risk assessment. Toxicology, 171(1):3-59.
doi: 10.1016/s0300-483x(01)00569-8 URL pmid: 11812616 |
| [20] |
Su W, Zhou Y, Ma Y, Wang L, Zhang Z, Rui C, Duan H, Qin Z , 2012. N'-Nitro-2-hydrocarbyliden-ehydrazinecarboximidamides: Design, synthesis, crystal structure, insecticidal activity, and structure- activity relationships. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 60(20):5028-5034.
doi: 10.1021/jf300616x URL pmid: 22546079 |
| [21] |
Von Stein RT, Silver KS, Soderlund DM , 2013. Indoxacarb, metaflumizone, and other sodium channel inhibitor insecticides: Mechanism and site of action on mammalian voltage-gated sodium channels. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 106(3):101-112.
doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2013.03.004 URL pmid: 24072940 |
| [22] |
Wang Y, He BJ, Zhao Q, Liang Z, Liu AX , 2006a. Effects of cyhalothrin on the transient outward potassium current in central neurons of Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Science, 13(1):13-17.
doi: 10.1111/ins.2006.13.issue-1 URL |
| [23] | Wang Y, He BJ, Wu CL, Liu AX , 2006b. Inhibition effects of cyhaliothrin on the delayed rectifier potassium current in the central neurons of Helicoverpa armigera. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 49(2):235-240. |
| [24] | Zhang MF, Fan JY, Zhang HW, Zhang XZ, Ma XG , 2009. Research development of studies on neonicotinoid insecticides. World Pesticides, 31(1):34-37, 64. |
| [ 张梅凤, 范金勇, 张宏伟, 张秀珍, 马新刚 , 2009. 新烟碱类杀虫剂的研究进展. 世界农药, 31(1):34-37, 64.] |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
