应用昆虫学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 814-822.doi: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2020.083
• 昆虫抗药性专栏 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2019-07-04
接受日期:2020-03-27
出版日期:2020-07-27
发布日期:2020-09-02
通讯作者:
刘景澜
E-mail:s18851449978@163.com;liujl@yzu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Li-Tong SUN( ), Ling FENG, Zi-Rui LIU, Xiao-Wei XU, Jing-Lan LIU***(
), Ling FENG, Zi-Rui LIU, Xiao-Wei XU, Jing-Lan LIU***( )
)
Received:2019-07-04
Accepted:2020-03-27
Online:2020-07-27
Published:2020-09-02
Contact:
Jing-Lan LIU
E-mail:s18851449978@163.com;liujl@yzu.edu.cn
摘要:
【目的】 海藻糖参与植物对逆境胁迫的响应与适应过程,本文旨在明确海藻糖对水稻生理生化特性及抗褐飞虱影响,将有助于全面探索海藻糖对水稻的潜在作用,为后续研究提供参考和依据。 【方法】 本实验在外施10 mmol?L –1和50 mmol?L –1浓度的海藻糖后,测定水稻超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)活性,丙二醛(MDA)和可溶性糖含量,褐飞虱取食后植株功能损失系数(FPLI)及利用刺吸电位技术(EPG)研究褐飞虱的取食行为。【结果】外施10 mmol?L –1和50 mmol?L –1浓度的海藻糖后,POD活性和可溶性糖含量显著上升,MDA含量显著下降,并且显著提高了水稻植株的功能损失指数,EPG结果发现海藻糖处理明显增加了N4波的持续时间。【结论】 适量的海藻糖改善水稻抗非生物胁迫的能力,但并不有利于对褐飞虱抗性的提高。
孙李曈, 冯玲, 刘子睿, 徐小伟, 刘景澜. 外源海藻糖对水稻生理生化及褐飞虱抗性的影响 *[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2020, 57(4): 814-822.
Li-Tong SUN, Ling FENG, Zi-Rui LIU, Xiao-Wei XU, Jing-Lan LIU. Effects of trehalose on the physiological and biochemical characteristics of rice, including resistance to the brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae)[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2020, 57(4): 814-822.
| 苗期受害等级(级) Injury grade at seedling stage (level) | 国际水稻研究所标准 The standard of International Rice Research Institute |
|---|---|
| 0 | 未受害 Unharmed |
| 1 | 受害很轻 Victimization is very light |
| 3 | 多数植株第1、第2叶变黄 The first and second leaves of most plants turn yellow |
| 5 | 植株明显变黄和矮化,或有半数以上植株枯萎、死亡 Plants become noticeably yellow and dwarfed, or more than half of the plants wither and die |
| 7 | 半数以上植株枯萎死亡,其余植株严重矮化,濒于死亡 More than half of the plants withered and died, and the remaining plants were severely dwarfed and were near death |
| 9 | 所有植株死亡 All plants die |
表1 水稻苗期对褐飞虱的抗性鉴定标准(巫国瑞等,1986)
Table 1 Identification criteria of rice resistance to brown planthopper at seedling stage (Wu et al., 1986)
| 苗期受害等级(级) Injury grade at seedling stage (level) | 国际水稻研究所标准 The standard of International Rice Research Institute |
|---|---|
| 0 | 未受害 Unharmed |
| 1 | 受害很轻 Victimization is very light |
| 3 | 多数植株第1、第2叶变黄 The first and second leaves of most plants turn yellow |
| 5 | 植株明显变黄和矮化,或有半数以上植株枯萎、死亡 Plants become noticeably yellow and dwarfed, or more than half of the plants wither and die |
| 7 | 半数以上植株枯萎死亡,其余植株严重矮化,濒于死亡 More than half of the plants withered and died, and the remaining plants were severely dwarfed and were near death |
| 9 | 所有植株死亡 All plants die |
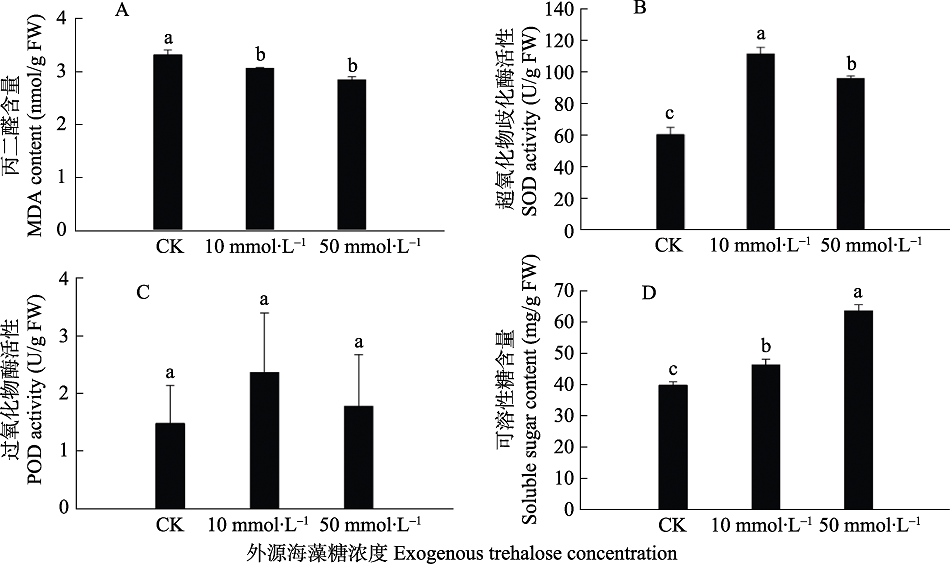
图1 外源海藻糖对水稻生理生化特性的影响 A.丙二醛;B. 超氧化物歧化酶;C. 过氧化物酶;D. 可溶性糖。 数据表示为平均值±标准误。柱上标有不同字母表示在0.05水平上的显着差异(LSD法)。下图同。
Fig. 1 Effects of exogenous trehalose on physiological and biochemical characteristics of rice A. Malondialdehyde (MDA); B.Superoxide dismutase (SOD); C. Peroxidase (POD); D. Soluble sugar. Data are means±SE. Histograms with the different letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 level by LSD test. The same below.
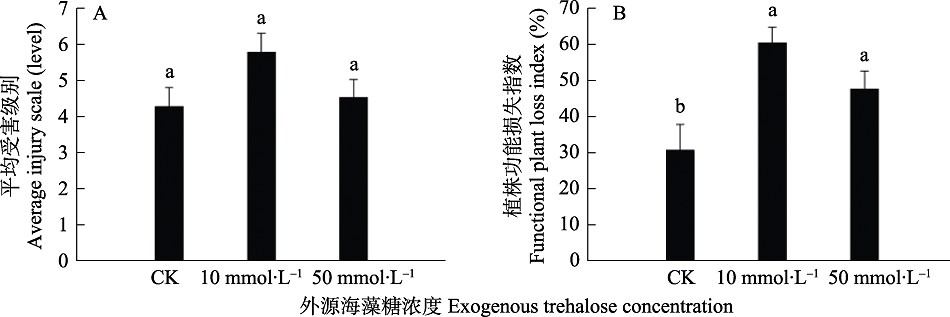
图2 褐飞虱取食后水稻的平均受害级别及植株功能损失指数(FPLI)测定 A. 水稻平均受害级;B. 植株功能损失指数(FPLI)。
Fig. 2 Average injury scale and plant function loss index of rice after fed by BPH A. Average injury scale; B. Functional plant loss index.
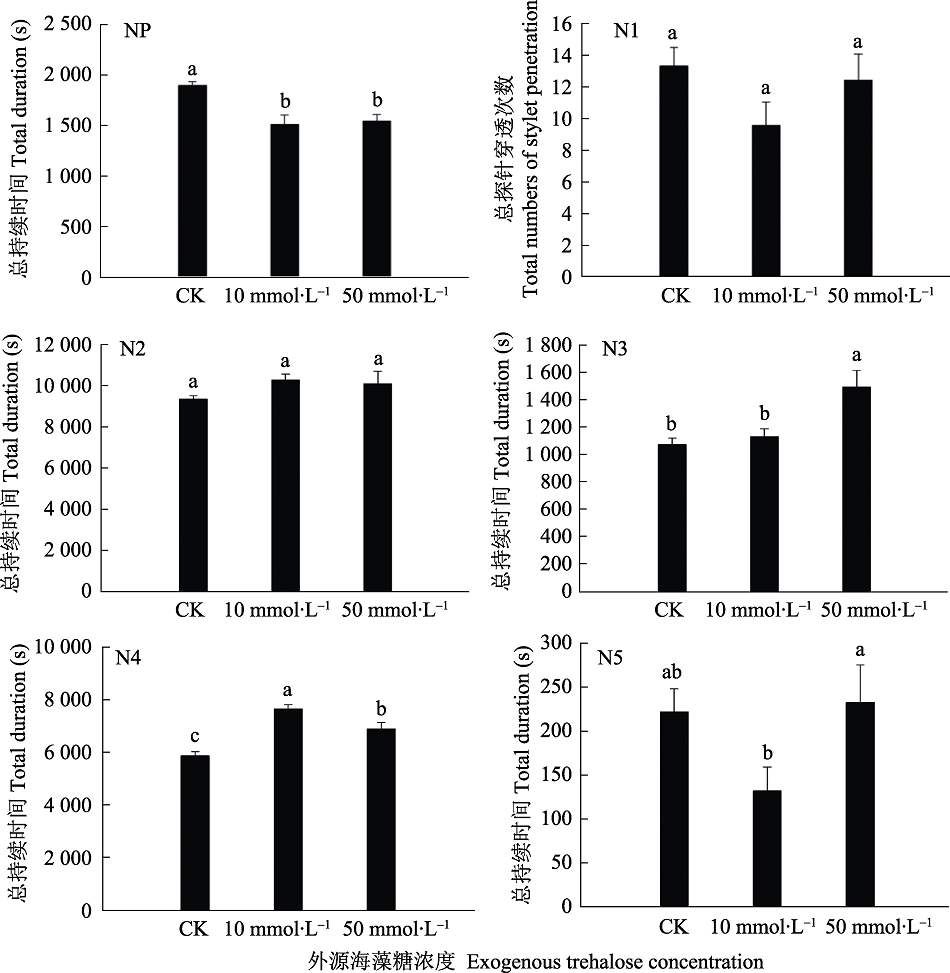
图3 褐飞虱在不同浓度海藻糖水稻上取食的EPG行为分析 NP:非刺探阶段的持续时间;N1:口针刺探次数;N2:口针在维管束移动的持续时间;N3:口针临近韧皮部细胞外移动的持续时间;N4:在韧皮部吸食汁液的持续时间;N5:吸食木质部汁液的持续时间。
Fig. 3 EPG analysis of BPH feeding behavior in rice treated with different concentrations of trehalose NP: The duration of non probing stage; N1: The number of probing; N2: The duration of trocar movement in vascular bundle; N3: The duration of phloem extracellular movement; N4: The duration of sucking sap in phloem; N5: The duration of sucking xylem sap.
| [1] |
Abebe T, Guenzi AC, Martin B, Cushman JC , 2003. Tolerance of mannitol-accumulating transgenic wheat to water stress and salinity. Plant Physiology, 131(4):1748-1755.
doi: 10.1104/pp.102.003616 URL pmid: 12692333 |
| [2] | Award M , 1990. Prospect of microencapusating red phosphorus. Chemistry Industry, ( 8):19-21. |
| [3] |
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I , 1971. Superoxide dismutase: Improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Analytical Biochemistry, 44(1):276-287.
doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8 URL pmid: 4943714 |
| [4] | Chen JM , 2004. Tolerance of rice varieties to brown planthopper damage and its physiological mechanism. Doctoral dissertation. Zhejiang: Zhejiang University. |
| [ 陈建明 , 2004. 水稻品种对褐飞虱为害的耐性及其生理机制研究. 博士学位论文. 浙江: 浙江大学.] | |
| [5] | Chen QY , 2017. Study on enhancement of tobacco resistance to common mosaic disease by exogenous trehalose. Master dissertation. Henan: Henan Agricultural University. |
| [ 陈芊伊 , 2017. 外源海藻糖增强烟草对普通花叶病抗性的研究. 硕士学位论文. 河南: 河南农业大学.] | |
| [6] | Cheng JA, Zhu ZR , 2006. Analysis on the key factors causing the outbreak of brown planthopper in Yangtze Area, China in 2005. Plant Protection, 32(4):1-4. |
| [7] |
Crowe JH, Carpenter JF, Crowe LM , 1998. The role of vitrification in anhydrobiosis. Annual Review of Physiology, 60(1):73-103.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.60.1.73 URL |
| [8] | Elbein AD , 1974. The metabolism of α, α-trehalose. Advances in Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biochemistry, ( 30):227-256. |
| [9] |
Gill SS, Tuteja N , 2010. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 48(12):909-930.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016 URL |
| [10] |
Goddijn O, Dun K , 1999. Trehalose metabolism in plants. Trends in Plant Science, 4(8):315-319.
doi: 10.1016/s1360-1385(99)01446-6 URL pmid: 10431221 |
| [11] |
Goddijn O, Smeekens S , 1998. Sensing trehalose biosynthesis in plants. Plant Journal, 14(2):143-146.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00140.x URL pmid: 9628011 |
| [12] | Govind SR, Sudisha J, Mostafa A, Shetty HS, Tran LP , 2016. Exogenous trehalose treatment enhances the activities of defense-related enzymes and triggers resistance against downy mildew disease of pearl millet. Frontiers in Plant Science, ( 7):1593. |
| [13] |
Hibino H , 1996. Biology and epidemiology of rice viruses. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 34(1):249-274.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.34.1.249 URL |
| [14] | Jing P, Bai SF, Liu F , 2013. Preliminary study on spike potential waveform of feeding behavior of Laodelphax striatellus. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 50(3):758-763. |
| [ 荆裴, 白素芬, 刘芳 , 2013. 灰飞虱取食行为刺吸电位波形的初步研究. 应用昆虫学报, 50(3):758-763.] | |
| [15] | Lei H, Xu RM , 1998. EPG study on feeding behavior of whitefly in greenhouse. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 41(2):113-123. |
| [ 雷宏, 徐汝梅 , 1998. 温室白粉虱取食行为的刺探电位(EPG) 研究. 昆虫学报, 41(2):113-123.] | |
| [16] | Li L, Huang QC, Qin GY , 2003. Research progress of trehalose in improving plant stress resistance. Bulletin of Biology, 38(6):6-7. |
| [ 李莉, 黄群策, 秦广雍 , 2003. 海藻糖在提高植物抗逆性方面的研究进展. 生物学通报, 38(6):6-7.] | |
| [17] | Li MY, Cao ZX, Yu XY , 2006. Effects of low temperature exercise on protective enzymes of cucumber seedlings under cold stress. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 15(1):160-164. |
| [ 李明玉, 曹辰兴, 于喜艳 , 2006. 低温锻炼对冷胁迫下黄瓜幼苗保护性酶的影响. 西北农业学报, 15(1):160-164.] | |
| [18] | Li YY, Liang GJ, Li YH, Ye QS , 2004. Effect of exogenous betaine on cold resistance of cucumber seedlings. Plant Physiology Communications, 40(6):673-676. |
| [ 李芸瑛, 梁广坚, 李永华, 叶庆生 , 2004. 外源甜菜碱对黄瓜幼苗抗冷性的影响. 植物生理学通讯, 40(6):673-676.] | |
| [19] |
Liu JX, Wang X, Li BP , 2010. Effects of exogenous nitric oxide donor SNP on ascorbic acid-glutathione cycle in ryegrass seedlings leaves under NaCl stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 19(2):82-88.
doi: 10.11686/cyxb20100212 URL |
| [ 刘建新, 王鑫, 李博萍 , 2010. 外源一氧化氮供体SNP对NaCl胁迫下黑麦草幼苗叶片抗坏血酸-谷胱甘肽循环的影响. 草业学报, 19(2):82-88.] | |
| [20] | Long ZL , 2014. The role of trehalose in plant response and adaptation to stress. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 449(16):4956-4959. |
| [ 龙正龄 , 2014. 海藻糖在植物对逆境胁迫响应与适应中的作用. 安徽农业科学, 449(16):4956-4959.] | |
| [21] | Luo C, Yue M, Xu HF, Zhang ZL , 2005. Application and progress of EPG technology in entomology research. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 48(3):437-443. |
| [ 罗晨, 岳梅, 徐洪富, 张芝利 , 2005. EPG技术在昆虫学研究中的应用及进展. 昆虫学报, 48(3):437-443.] | |
| [22] |
Ma C, Wang ZQ, Kong BB, Lin TB , 2013. Exogenous trehalose differentially modulate antioxidant defense system in wheat callus during water deficit and subsequent recovery. Plant Growth Regulation, 70(3):275-285.
doi: 10.1007/s10725-013-9799-2 URL |
| [23] | Ma GS, Yang J, Lian H, Wang RH, Wu X , 2010. Effects of trehalose on osmotic regulators and enzyme activities of tomato under salt stress. Northern Horticulture, ( 6):59-61. |
| [ 马光恕, 杨瑾, 廉华, 王茹华, 吴瑕 , 2010. 盐胁迫下海藻糖对番茄渗透调节物及酶活性的影响. 北方园艺, ( 6):59-61.] | |
| [24] | Madan S , 2015. Trehalose mitigates heat stress-induced damages in wheat seedlings. Journal of Wheat Research, 7(1):74-78. |
| [25] | Miao J, Han BY , 2008. DC-EPG analysis on effect of tea plant induced by methyl salicylate against feeding of tea green leafhopper. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 35(2):143-147. |
| [26] |
Olivier F, Linda B, Anthony Q, Rajbir SS, Christophe C , 2010. Trehalose and plant stress responses: Friend or foe? Trends in Plant Science, 15(7):409-417.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.04.004 URL |
| [27] | Pang CP, Ye L, Ma J, Lu T, Yang ZY, Qi MF , 2017. Regulation of trehalose on photosynthesis of tomato seedling leaves under high temperature. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 45(21):151-154. |
| [ 庞椿朋, 叶亮, 马健, 路涛, 杨宗艺, 齐明芳 , 2017. 海藻糖对高温下番茄幼苗叶片光合作用的调控作用. 江苏农业科学, 45(21):143-146.] | |
| [28] | Peng GS , 2011. Preliminary study on resistance mechanism of different rice varieties to laodelphax striatellus. Master thesis. Henan: Henan Normal University. |
| [ 彭高松 , 2011. 不同水稻品种对灰飞虱抗性机理的初步研究. 硕士学位论文. 河南:河南师范大学.] | |
| [29] | Quan RL, Wang QL, Ma HY, Fu D, Huo EW, Shen GH, Guo GY , 2015. Effects of drought on rice growth and development and research progress on drought resistance. China Seed Industry, ( 9):12-14. |
| [ 全瑞兰, 王青林, 马汉云, 扶定, 霍二伟, 沈光辉, 郭桂英 , 2015. 干旱对水稻生长发育的影响及其抗旱研究进展. 中国种业, ( 9):12-14.] | |
| [30] |
Simms EL , 2000. Defining tolerance as a norm of reaction. Evolutionary Ecology, 14(4):563-570.
doi: 10.1023/A:1010956716539 URL |
| [31] |
Strauss SY, Agrawal AA , 1999. The ecology and evolution of plant tolerance to herbivory. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 14(5):179-185.
doi: 10.1016/s0169-5347(98)01576-6 URL pmid: 10322530 |
| [32] |
Velusamy R, Heinrichs EA , 1986. Electronic monitoring of feeding behavior of Nilaparvata lugens(Homoptera: Delphacidae) on resistant and susceptible rice cultivars. Environmental Entomology, 15(3):678-682.
doi: 10.1093/ee/15.3.678 URL |
| [33] |
Wiemken A , 1990. Trehalose in yeast, stress protectant rather than reserve carbohydrate. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 58(3):209-217.
doi: 10.1007/BF00548935 URL pmid: 2256682 |
| [34] | Wu GR, Tao LY, Chen FY, Hu GW , 1986. Discussion on screening methods of rice resistance to white-backed planthopper. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 29(4):453-455. |
| [ 巫国瑞, 陶林勇, 陈福云, 胡国文 , 1986. 水稻对白背飞虱抗性筛选方法的探讨. 昆虫学报, 29(4):453-455.] | |
| [35] | Xiao YF, Zhang CZ, Gu ZY , 2001. Resistance mechanism of rice varieties to white-backed planthopper. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 28(3):198-202. |
| [ 肖英方, 张存政, 顾正远 , 2001. 水稻品种对白背飞虱的抗性机理. 植物保护学报, 28(3):198-202.] | |
| [36] | Xu T, Zhou CY, Zhou C, Zhao S, Wu LL, Tan KF , 2014. Effects of trehalose on antioxidant system of muskmelon seedlings under salt stress. Northern Horticulture, ( 19):28-30. |
| [ 徐婷, 周传余, 周超, 赵索, 武琳琳, 谭可菲 , 2014. 海藻糖对盐胁迫下薄皮甜瓜幼苗抗氧化系统的影响. 北方园艺, ( 19):28-30.] | |
| [37] |
Xue J, Bao YY, Li BL, Cheng YB, Peng ZY, Liu H, Xu HJ, Zhu ZR, Lou YG, Cheng JA, Zhang CX , 2010. Transcriptome analysis of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. PLoS ONE, 5(12):e14233.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014233 URL pmid: 21151909 |
| [38] | Yang SJ , 2005. Resistance of hybrid offspring of medicinal wild rice to Cnaphalocrocis medinalis. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 33(4):570. |
| [ 杨士杰 , 2005. 药用野生稻杂交后代对稻纵卷叶螟的抗性. 安徽农业科学, 33(4):570.] | |
| [39] | Yang SH , 2006. Effects of salt stress on plants and the mechanism of salt tolerance. World Sci-tech R&D, 28(4):70-76. |
| [40] | Zhao KF , 1993. Salt Tolerance Physiology of Plants. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press. 25-30. |
| [ 赵可夫 , 1993. 植物抗盐生理. 北京: 中国科技出版社. 25-30.] |
| [1] | 李雪梅, 郑晓旭, 何帅洁, 杨凤连, 吴刚. 不同农事操作技术对稻田害虫和天敌种群动态的影响 *[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2020, 57(1): 105-112. |
| [2] | 郑晓旭, 赵慕华, 何帅洁, 李雪梅, 杨凤连, 吴刚. 华中地区五种水稻品种对褐飞虱生活史和种群动态的影响 *[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2020, 57(1): 142-152. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
